Reference13r2:Services/SNMP
The VoIP device allows the operating state to be monitored using SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol with version 1 and 3). Standard MIB II and a manufacturer-specific MIB (Management Information Base) are supported. Detailed information about this MIB can be obtained from a certified innovaphone dealer or downloaded directly in the download area of the innovaphone homepage. It is included in the folder "tools" of the "apps" package together with other applications and firmware. File name: INNO-MIB-V7.TXT (http://download.innovaphone.com/ice/6.00/).
innovaphone uses the standard Ports for SNMP, UDP Port 161 and UDP Port 162 for SNMP traps, and they are not changeable.
Note: SNMP traps will not be send before an uptime of 90 seconds(will be collected in this time). Due to DHCP negotiation awaiting
| Enable: | Enable the SNMP service (default: deactivated). |
| Enable SNMPv1: | SNMPv1 must be explicitely activated (default: deactivated). |
| Community: | If the standard community name public is not being used, a different community name can be entered in this field. |
| Device Name: | For more detailed information, a device name can be specified here for the SNMP agent. |
| Contact: | As can a contact person (Contact). |
| Location: | As can a location (Location). |
| Authentication Trap: | Access via SNMP is only possible if the correct community name is entered. If this check box is checked, a trap is generated in the case of access with an incorrect community name. |
| Trap Destination: | Destinations for trap messages also have to be defined if the device is to trigger the traps defined in the manufacturer-specific innovaphone MIB. |
| Allowed Networks: | To increase security, access to the device can be restricted by restricting SNMP access to a defined list of computers or IP address ranges. To disable SNMP access completely just enter 0.0.0.0 as Address and 255.255.255.255 as Mask. |
| SNMPv3/Engine ID: | Informative: This agent's engine id according to RFC3411 |
| SNMPv3/Authentication: | Choose from MD5, SHA1. A selection of NONE will force the encryption setting to NONE, also. |
| SNMPv3/Encryption: | Choose from DES, AES128. |
| SNMPv3/User,Password(Auth),Password(Crypt): | Enter the credentials for this agent's authoritative engine. Two different passwords are configurable. One password for authentication and a different one for privacy/encryption. |
In V7 the SNMP Traps are enhanced
All events with type =Alarm are send via SNMP traps. SNMP Trap delivers: code,severity,txt (e.g interface down) and Alarm –source (e.g IP0/ETH1)
innoDiagAlarm TRAP-TYPE
ENTERPRISE innovaphone
VARIABLES {
trapGaugeParm, -- Alarm Code
trapDisplayStringParm, -- Alarm Source
trapGaugeParm, -- Severity: indeterminate(0),major(1),critical(2)
trapDisplayStringParm -- Alarm Text
}
DESCRIPTION
"This trap corresponds to an alarm under Administration/Diagnostics/Alarms"
::= 6
innoDiagAlarmClear TRAP-TYPE
ENTERPRISE innovaphone
VARIABLES {
trapGaugeParm, -- Alarm Code
trapDisplayStringParm -- Alarm Source
}
DESCRIPTION
"This trap corresponds to an alarm clearing under Administration/Diagnostics/Alarms"
::= 7
Testing SNMPv3 from a Linux host
The following tests are based on Debian 9.
snmpwalk
Under Linux you can use snmpwalk to check the connection and read the OID tree. Replace the variables in the square brackets with the values of the snmp configuration on the innovaphone gateway.
- snmpwalk -v 3 -a SHA -A [Password(Auth)] -l authPriv -u [User] -x AES -X [Password(Crypt)] [IP address]
SNMPv3 Traps
Under Linux you can receive SNMPv3 traps using snmptrapd. The following example shows a snmptrapd.conf in /etc/snmp/. Replace the variables in the square brackets with the values of the snmp configuration on the innovaphone gateway.
createUser -e [engineID] [User] SHA [Password(Auth)] AES [Password(Crypt)]
authUser log,execute,net [User] priv
Now the snmptrapd daemon must be activated and started.
- systemctl enable snmptrapd.service
- systemctl start snmptrapd.service
After a restart of the snmptrapd daemon it should listen on Port 162 and you can receive the traps in syslog. Also make sure that the Linux firewall does not block ports 161 and 162.
- netstat -ntulp | grep :162
udp 0 0 0.0.0.0:162 0.0.0.0:* 28086/snmptrapd
- tail -f /var/log/syslog
Alternatively you can start snmptrapd directly from the command line. The events are displayed directly on the console. The snmptrapd service must be stopped before.
- systemctl stop snmptrapd.service
- snmptrapd -f -Lo
Important Note: After each change to /etc/snmp/snmptrap.conf, you must also clean up /var/lib/snmp/snmptrapd.conf (or /var/net-snmp/snmptrapd.conf). Scroll down! There are many blank rows in it. This persistent file is automatically created and used when smnptrapd starts, but is not automatically cleaned. Because of the required write permissions to this directory, snmptraced must be started as root.
Helpful documents
https://support.nagios.com/kb/article/snmp-trap-snmptrapd-service-88.html
Testing from a Windows host
iReasoning MIB Browser Professional could be a good choice. The program also includes a SNMPv3 Trap Recorder.
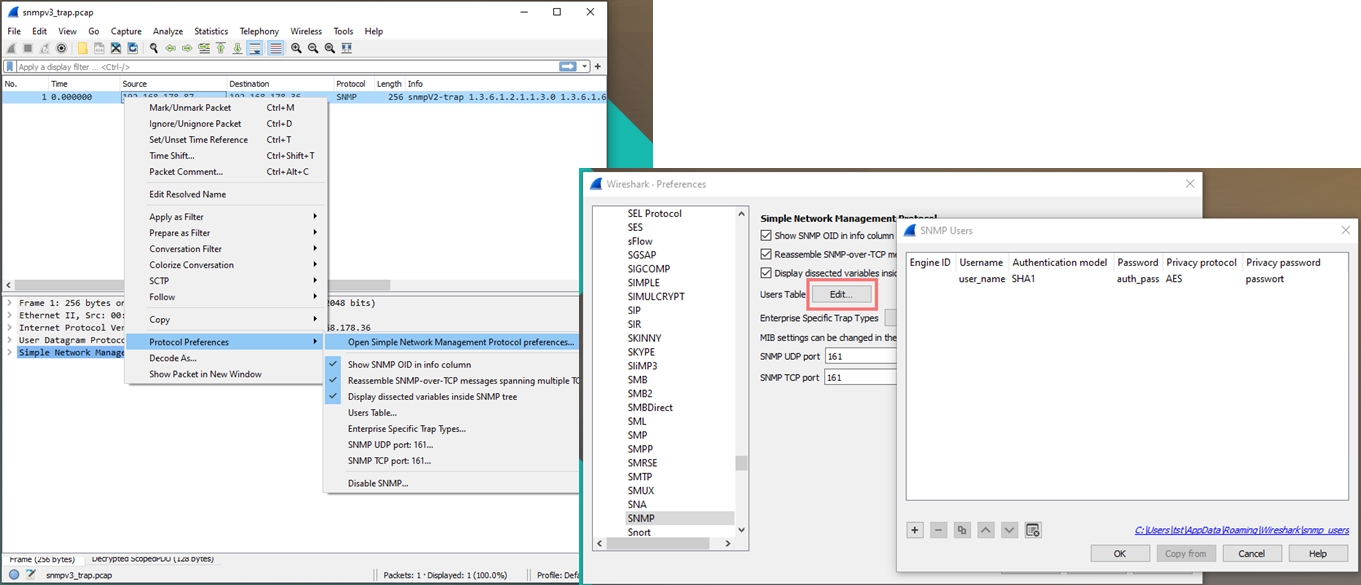
Decoding of encrypted SNMPv3 packets in Wireshark
Encrypted SNMPv3 packets can be decrypted by setting the credentials in the Wireshark Protocol Preferences.