Reference10:Concept Softwarephone
General
Innovaphone SoftwarePhone is the implementation of innovaphones HW phones software as a Windows process. So all the features native to the hardwarephones are present in SoftwarePhone as well. SoftwarePhone has no UI, it is operated via myPbx.
System Requirements
The innovaphone SoftwarePhone requires Windows Vista, Windows 7 or later.
Installation
Prior to installing the 10.00 Version of innovaphone SoftwarePhone an eventually installed 9.00 version must be manually deinstalled. From version 10.00 on, subsequent releases can be updated without first deinstalling the older version. When updating the installation, the previous configuration (if existing) is reused. Otherwise a default configuration is installed.
The following items are installed:
- SoftwarePhone .exe and related files (dll) in Program files (x86)\innovaphone\SoftwarePhone
- Hid.tbl (the code definitoins of supported USB headsets) in Program files (x86) \innovaphone\SoftwarePhone
- The config files „swphone_config.cfg“ und „swphone_command.cfg” in the User Roaming directory (if no previous configuration is located there, otherwise the old configuration is used)
Installation Process:
- http port 80 ist checked to be available as the SoftwarePhone ’s web configuration port. If not free, a search starting at port 10006 is executed to find a free port. The URL file, containing the configuration servers web @ is adjusted to the determined free port
- SoftwarePhone is startet.
Configuration
The configuration is opened by selecting “Configuration” from the start menu. A browser connection is opend to the server running as part of SoftwarePhone and the configuration menu is displayed. The configuration options are the same as for the hardware phones with a few specifics referring to SoftwarePhone running as a Windows process:
- User Configuration
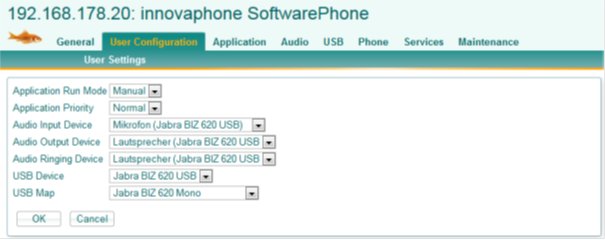
This tab is unique in the way that it can only be accessed from the computer SoftwarePhone is running on. Here the typical End User Configurations are set: Audio, USB-headset and process operational parameters.
- Application
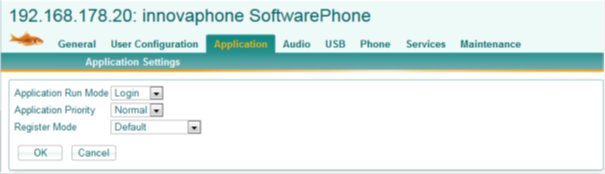
The Applicatons run mode and priority can be set and wheter to register with the computers name at the PBX.
- Audio
The desired audio devices can be selected.
- Audio
The Audio –Input, -Output and –Ringing device can be selected.
- USB
To use the USB headsets function buttons here the device and appropriate map are selected.
[Tab: „User Configuration"]
This tab is unique in the way that it can only be accessed from the computer SoftwarePhone is running on. Here the typical End User Configurations are set: Audio, USB-headset and process operational parameters.
Application Run Mode:
- Manual: SoftwarePhone needs to be started manually
- Login: SoftwarePhone will be started when the user logs in (like myPbx).
Application Priority:
- Normal: SoftwarePhone runs at standard Windows process priority. Usually sufficient. If SoftwarePhone runs on a less powerful computer and voice delays are experienced the setting to :
- High: will lead to a better processing oft he rtp streams.
NOTE: The actual process priority can be viewed with taskmgr.exe
Audio Input Device:
The microphone selection.
Audio Output Device:
The speaker selection
Audio Ringing Device:
The Ringing device selection
[Tab: "USB”]
USB Device:
The USB headset selction.
USB Map:
The codepage selection for the selected usb device. Here one or two choices are presented. If a selection item that refers to the selected USB Device use this. If only “generic HID Telephonie Page” is available you can try to use the headsets button (some headsets support the generic codes)
NOTE: If the headsets buttons do not work for call control, then call control is solely available through myPbx. Nevertheless the USB headset can be used as the audio-in/output device.
[Tab:„Application“]
Admin mode Application configuration.
Application Run Mode, Application Priority: see „User Configuration“
Register Mode:
- Default: Registration modes like the HW phones.
NOTE: Anonymous registration might not work in all environments, especially those that prevent multicasts. For example, when using SoftwarePhone over a vpn connection ensure that multicast forwarding is guaranteed. Also, if a virtual machine is running on the same computer it might prevent multicasts being sent on the LAN.
- Computername:
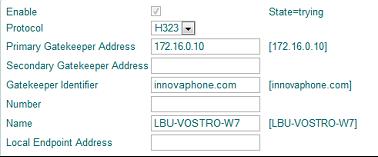
The best way for registering SoftwarePhone at the PBX. It uses the computername as it is visible on the LAN. The computername is determined by SoftwarePhone and the appropriate parameters are set for the “Phone” modul. This configuration appears in the field “Name” under the “Phone” tab (Example for computer„LBU-VOSTRO-W7“ ):
[Tab:"Audio”]:
Admin mode Audio configuration. Items see „User Configuration“
[Tab:“USB”]:
Admin mode Audio configuration. Items see „User Configuration“
Rollout
Especially in larger installations it is desirable to have a mechanism for automatic configuration of the SoftwarePhones. This can be accomplished in the following way:
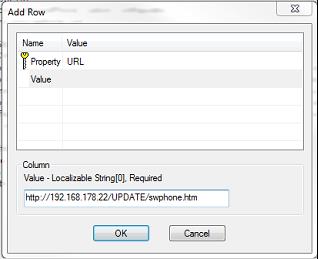
SoftwarePhones installation package (softwarephone .msi)can be parametrized by creating an Orca MSI database editor transform with the parameters: URL and POLL. Theses parameters are entered in the “Property” table
It is recommended that the “POLL” value be set to “1” (shortest time: 1minute). When SoftwarePhone is installed with the transform it starts, waits 1 min (poll period) then accesses the script file specified in the “POLL” parameter and executes the commands therein. To register SoftwarePhone with the computername at the PBX the script file should look as follows (example showing the PBX @ “192.168.178.22” with the identifier „IP800-06-25-6e” :
… #set the PBX @ and Identifier config change PHONE SIG /prot H323 /gk-addr 192.168.178.22 /gk-id IP800-06-25-6e
#register with computername mod cmd APP0 app-set /op OK /reg_mode ComputerName
#reset the automatic configuration update config add UP1 /url
#reset SoftwarePhone and apply config reset
Another method to provide configurations to the installed SoftwarePhone s is preparing a configuration template by configuring one SoftwarePhone entity, then using the generated “swphone_commands.cfg” file in the <users roaming directory >\innovaphone\SoftwarePhone as the template, copying it to the update location and using it in the script file:
#invoke configuration template mod cmd UP0 cfg <update directory location>/swphone_commands.cfg
This method is particularly helpful when many USB headset of the same type are used.
Supported USB headsets
The following USB headsets are supported for onhook/offhook functionality:
- innovaphone IP 10 (I)
- innovaphone IP 10 (II)
- Handset for Voip (Couple) (ZMM)
- Handset for Voip (Internet) (ZMM)
- Claritel-i750 - vp (generated)
- GN 8120 USB
- Plantronics CS50/CS60-USB Headset
- GN 9350
- GN 9335e USB port
- Jabra A330 device 2
- Jabra BIZ 2400
- Jabra LINK 320 USB
- Jabra LINK 350 USB
- Jabra LINK 360 USB
- Jabra PRO 9460 (1041)
- Jabra PRO 94(60/70) (1042)
- Jabra GO 6470 (1003)
- Jabra GO 6470 (1004)
- Jabra PRO 930 (930-25-509-101)
- Jabra LINK 350 OC
- Jabra GO 6430 (6430-17-20-201) | Version C
- Jabra SUPREME UC (5078-230-310)
- Plantronics Savi 740
- Sennheiser VoIP USB headset
- Sennheiser DECT
- Sennheiser CEHS-CI 02
- Jabra SPEAK 410 USB Mono
- Jabra SPEAK 410 USB Stereo
- Jabra BIZ 2400 Mono USB
- Jabra BIZ 2400 USB Mono
- Jabra BIZ 2400 USB Mono (2)
- Jabra PRO 9450
- Jabra PRO 9450 (2)
- Jabra BIZ 620 Mono
- Jabra UC Voice 550 Duo(5599-829-209)
- Jabra UC Voice 550 Mono(5593-829-209)
- Jabra LINK 280(280-09)
- Jabra LINK 14201-30 (DHSG-USB Adapter)
- GN Netcom Jabra 2000 USB Duo NC EMEA
- GN2000 Stereo USB
- Plantronics - Voyager PRO UC v2 (USB/bluetooth)
- Plantronics - CALISTO P420 USB
- Plantronics - Voyager PRO UC v2 (USB/bluetooth) (2)
- Plantronics - Blackwire C320 (85619-02)
- Plantronics - Blackwire C720 (87506-02)
- Plantronics - DA45 (USB/Wired)
- Plantronics - Blackwire C620 (USB/Wired)
- Plantronics - C420 (product aa10)
- Plantronics - C420 (product aa14)
- Plantronics - C435 (P.N. 85800-05)
- Plantronics D100 (USB/Bluetooth, Savi W430, W440)
Troubleshooting Connectivity Problems
If you experience problems with softwarephone attaching to the PBX or not being able to make calls please check the following:
- check in the “Phone” tab whether the state is “up”
- check in the “General” tab if License is “Valid”
- Start a command window as Administrator and issue a “netstat –a –b > swphone_netstat.txt
In the “swphone_netstat.txt” file search for “1720”. There should be an entry like this:
TCP 0.0.0.0:1720 LBU-VOSTRO-W7:0 LISTENING [softwarephone.exe].
Please search for other occurances of “1720” to ensure that no other processes listen to this port.
- Make a softwarephone trace to see if the packets are received by softwarephone
In the “Maintenance” tab “Tracing” enable “H.323 Signaling”, “Phone” and “All TCP/UDP Traffic”. Then try to make the call. In the resulting trace you should see the events like the following:
0:0103:337:3 - RECV RESULT[](662 from pla(192.168.178.22:60003) type: 1) 0:0103:337:3 - PHONE_LISTEN.1 -> PHONE_REG.1 : SIG_SETUP faststart=3ac8bec cmd=PROPOSAL cdpn=400
If these events are no present in the trace it could be that the firewall settings prevent some of softwarephone’s functions. This could be the Firewall.
- Check the firewall settings for softwarephone
Please open the “System Administration\Windows-Firewall\Allow Program.. Ensure that softwarephone is enabled on the required interfaces. If this doesn’t solve the problem then temporaryly disable the firewall completely and try again. Now even with the firewall disabled there could be some other security software that causes the problem. To find out if packets to the “h323hostcall” port (1720) are filtered by the firewall you can use the commands “netsh wfp capture start” to start a trace of the test and “netsh wfp capture stop” to stop the trace. The trace is written into the file: “wfpdiag.cab” . Extract the file: “wfpdiag.xml”. In this file search for “1720”. If the packet is filtered by the firewall an entry like the following can be found:
<netEvent> <header> <timeStamp>2013-11-05T11:20:27.367Z</timeStamp> <flags numItems="8"> <item>FWPM_NET_EVENT_FLAG_IP_PROTOCOL_SET</item> <item>FWPM_NET_EVENT_FLAG_LOCAL_ADDR_SET</item> <item>FWPM_NET_EVENT_FLAG_REMOTE_ADDR_SET</item> <item>FWPM_NET_EVENT_FLAG_LOCAL_PORT_SET</item> <item>FWPM_NET_EVENT_FLAG_REMOTE_PORT_SET</item> <item>FWPM_NET_EVENT_FLAG_APP_ID_SET</item> <item>FWPM_NET_EVENT_FLAG_USER_ID_SET</item> <item>FWPM_NET_EVENT_FLAG_IP_VERSION_SET</item> </flags> <ipVersion>FWP_IP_VERSION_V4</ipVersion> <ipProtocol>6</ipProtocol> <localAddrV4>192.168.178.21</localAddrV4> <remoteAddrV4>192.168.178.22</remoteAddrV4> <localPort>1720</localPort> <remotePort>60007</remotePort> <scopeId>0</scopeId> <appId>
…
<asString>...</asString>
</appId> <userId>S-1-5-21-3364624427-3176291796-194291593-006</userId> </header> <type>FWPM_NET_EVENT_TYPE_CLASSIFY_DROP</type> <classifyDrop> <filterId>105267</filterId> <layerId>44</layerId> <reauthReason>0</reauthReason> <originalProfile>2</originalProfile> <currentProfile>2</currentProfile> </classifyDrop> </netEvent>
where the <localAddrV4>192.168.178.21</localAddrV4> and the <remoteAddrV4>192.168.178.22</remoteAddrV4> should be your computers and the PBX’s @.
- Check if the setup from the PBX is received at the local computer and what happens with it
Sometimes, Antivirus Packages can implement their own network access policy. This can result in a h323 release complete with cause “User Busy” to an incoming Setup from the PBX before any other softwarephone is reached. To see which process Sends/Receives the packets in a flow you can use the “netmon”, Microsofts free Packet tracer.