Reference12r1:Concept Netlogon Windows Authentication
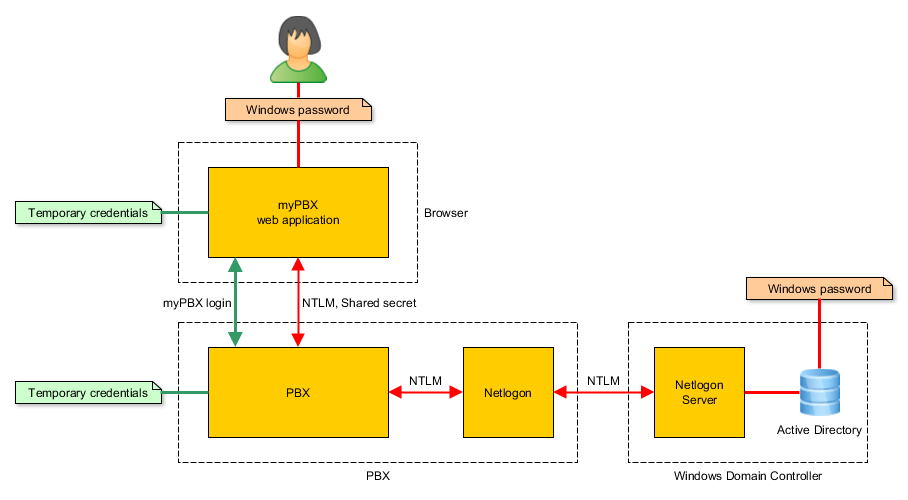
Netlogon can be used to verify user credentials against a Windows domain controller. myPBX can use this service to allow users to login with their Windows password.
Applies to
- innovaphone devices with a PBX from version 12r1.
How it works
The netlogon service passes NTLM hashes to a windows domain controller for verification. myPBX uses the netlogon service for user authentication using windows passwords.
Connection to the domain controller
The netlogon service needs to connect to the DC. It authenticates using a computer account in the domain.
- DNS is used to retrieve the IP address of the DC (SRV record for _ldap._tcp.example.com).
- The endpoint mapper on the DC is asked for the actual port of the netlogon server on the DC.
- A connetion is established to the netlogon server. For authentication the configured computer name and computer password is used.
Login with windows password in myPBX
The login process using windows credentials works in two steps. First an NTLM handshake is done, involving the netlogon service on the PBX and the windows domain controller. As a result the PBX creates temporary credentials that can be used by the web application for normal login in the second step.
NTLM handshake
The NTLM challenge-response mechanism is used to verify the windows password of the user against the Active Directory. For that only hash values are transmitted between the web application and the PBX. So the windows password is never transmitted or stored.
- The PBX chooses an NTLM challenge and sends it to the browser.
- The web application asks the user for the windows credentials and calculates an NTLM response. The response is sent back to the PBX.
- The PBX asks the netlogon service, if the NTLM response is valid for the given NTLM challenge.
- The netlogon service forwards the request to the domain controller.
- The domain controller verifies the NTLM response. It can do so because it has access the required information that is located in the Active Directory. Then it tells the netlogon service if the login was OK.
- The netlogon service forwards the login result to the PBX.
- If the login was OK the PBX creates temporary credentials for the user. They consist of a random username and a random password that is associated with the user object in the PBX. That alias is sent to the web application in an encrypted message.
Actual login
For the actual login, myPBX uses the temporary credentials that were created during the NTLM handshake. The PBX deletes the temporary credential when the user logs-out again.
Requirements
Windows domain
- A computer account for the innovaphone device with a known password.
- User authentication using NTLM must be enabled.
Device
- Firmware from version 12r1.
- Working DNS configuration.
PBX
- The usernames (Name) of the user objects in the PBX must match the Windows user name (samAccountName).
- Netlogon authentication must be enabled on the myPBX configuration page.
Security considerations
- As NTLM hashes are not very secure, HTTPS should be used for the communication between myPBX and the PBX.
Configuration
Usage
Tracing and logging
The log gives basic information about up and downtime of the service and the NTLM handshakes that are done.
LOG NETLOGON 0 Service up LOG NETLOGON 0 Authentication for 'exampleuser' failed (error c0000064) LOG NETLOGON 0 Service down
The trace contains more detailed information for tracking down problems and all the exchanged protocol messages. The protocol messages have been removed in the following example for better readability.
NETLOGON: state ABORT NETLOGON: state RECONNECT NETLOGON: starting Domain(example.com) Computer(PBX-NETLOGON) ComputerPassword(XXX) NETLOGON: state DNS NETLOGON.0 -> dns.0 : DNS_GETHOSTBYNAME example.com ctx=0x0 flags=0x1 port=0 dns.0 -> NETLOGON.0 : DNS_GETHOSTBYNAME_RESULT ctx=0x0 result=0 addr=172.16.0.5 port=389 NETLOGON: state EPM_CONNECT NETLOGON: connect to endpoint mapper at 172.16.0.5:135 (dc-w2k8.example.com) NETLOGON: state EPM_BIND_HEAD NETLOGON: state EPM_BIND_BODY NETLOGON: state EPM_MAP_HEAD NETLOGON: state EPM_MAP_BODY ........ NETLOGON: state EPM_DISCONNECT NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_CONNECT NETLOGON: connect to netlogon_service at 172.16.0.5:49159 (dc-w2k8.example.com) NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_BIND_HEAD NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_CHALLENGE_HEAD NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_CHALLENGE_BODY .... NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_AUTHENTICATE_HEAD NETLOGON: encryption parameters ClientChallenge(e5cb2fd5f5218531) ServerChallenge(7338e9e65867e383) SessionKey(0978a50b44003835ac420ae6e69dfa89) NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_AUTHENTICATE_BODY NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_ALTER_HEAD NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_ALTER_BODY NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_DUMMYROUTINE_HEAD NETLOGON: state NETLOGON_DUMMYROUTINE_BODY NETLOGON: state CONNECTED NETLOGON.0 -> NETLOGON.0 : NETLOGON_NTLM(0, exampleuser) challenge: 86fee2c0fa1e6ee6 nt_response: 58881d894b81835edd0bfe758e468a0a0cd553e8c9f7a702 lm_response: 09e25853e618688157c0faadb0861818f367056548ea9496 NETLOGON: start authentication Username(exampleuser) Challenge(86fee2c0fa1e6ee6) NtResponse(58881d894b81835edd0bfe758e468a0a0cd553e8c9f7a702) LmResponse(09e25853e618688157c0faadb0861818f367056548ea9496) NETLOGON: state AUTHENTICATE_HEAD NETLOGON: state AUTHENTICATE_BODY d... NETLOGON: authentication failed (error c0000064) NETLOGON: state CONNECTED NETLOGON.0 -> NETLOGON_SOCKET.44 : SOCKET_RECV(16) NETLOGON.0 -> NETLOGON.0 : NETLOGON_NTLM_RESULT(0, FAILED, c0000064, )