Reference:DHCP client: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
These configurations include | These configurations include | ||
{| border=1 | |||
| H323 Gatekeeper | |||
The IP addresses of the main and alternate gatekeeper. IP200 only | | The IP addresses of the main and alternate gatekeeper. IP200 only | ||
|- | |||
| H323 Gatekeeper ID | |||
| The ID of the gatekeeper taking care of the device. IP200 only | |||
The ID of the gatekeeper taking care of the device. IP200 only | |- | ||
|POSIX Time zone | |||
|The time zone string defining the time zone the device lives in (see the ''VoIP Gateways 5.0'' Manual, chapter 9.1.3 for more details about time zone settings) | |||
|- | |||
The time zone string defining the time zone the device lives in (see the | |Default coder | ||
|The coder the device will try negotiate during media stream setup. IP200 only | |||
|- | |||
|Language | |||
The coder the device will try negotiate during media stream setup. IP200 only | | The user interface language of the device. IP200 only | ||
|- | |||
|Location | |||
|The location information (country code, area code etc.). IP200 only | |||
The user interface language of the device. IP200 only | |- | ||
|VLAN ID | |||
| The VLAN ID for voice traffic | |||
|- | |||
The location information (country code, area code etc.). IP200 only | |VLAN Priority | ||
| The VLAN Priority for voice traffic | |||
|- | |||
|TOS Bits | |||
The VLAN ID for voice traffic | | The value for the IP TOS field in the IP header of voice traffic | ||
|- | |||
|Enbloc dialling | |||
| Overlapped sending disabled. IP200 only | |||
The VLAN Priority for voice traffic | |- | ||
|Dialtone type | |||
| The type of locally generated dial tones. IP200 only | |||
|- | |||
The value for the IP TOS field in the IP header of voice traffic | |Faststart | ||
| Disable/Enable the H245 faststart procedure | |||
|- | |||
|H245-Tunnelling | |||
Overlapped sending disabled. IP200 only | | Disable/Enable H245 tunneling | ||
|- | |||
|Clock type | |||
| Format of date and time display. IP200 only | |||
The type of locally generated dial tones. IP200 only | |- | ||
|Static routes | |||
| Additional static routes | |||
|- | |||
Disable/Enable the H245 faststart procedure | |Configuration parameters for the update server | ||
| URL to retrieve update commands from and poll interval | |||
|- | |||
|LDAP directory configuration | |||
Disable/Enable H245 tunneling | |Parameters to access an external LDAP directory. IP200 only | ||
|} | |||
Format of date and time display. IP200 only | |||
Additional static routes | |||
URL to retrieve update commands from and poll interval | |||
Parameters to access an external LDAP directory. IP200 only | |||
| Line 115: | Line 100: | ||
First you need to create a new vendor class. | First you need to create a new vendor class. | ||
Use the | Use the ''Define Vendor Class…'' / ''Herstellerklasse definieren'' menu entry on the DHCP server’s context menu | ||
[[Image:How_to_use_the_innovaphone_DHCP_client_Dhcp1_conv.JPG]] | [[Image:How_to_use_the_innovaphone_DHCP_client_Dhcp1_conv.JPG]] | ||
| Line 127: | Line 112: | ||
Anzeigename / Display name innovaphone | {| | ||
| Anzeigename / Display name || innovaphone | |||
Beschreibung / Description innovaphone VoIP Options | |- | ||
| Beschreibung / Description || innovaphone VoIP Options | |||
Kennung / ID (ASCII) 1.3.6.1.4.1.6666 | |- | ||
| Kennung / ID || (ASCII) 1.3.6.1.4.1.6666 | |||
|} | |||
Add the innovaphone options. Use the | Add the innovaphone options. Use the ''Configure predefined options'' / ''Vordefinierte Optionen einstellen'' entry in the DHCP server’s context menu | ||
[[Image:How_to_use_the_innovaphone_DHCP_client_Dhcp3_conv.JPG]] | [[Image:How_to_use_the_innovaphone_DHCP_client_Dhcp3_conv.JPG]] | ||
| Line 142: | Line 128: | ||
Name | {| | ||
|+ | |||
H323 gatekeeper | | Name || Data type || Array || Code | ||
|- | |||
H323 gatekeeper id | | H323 gatekeeper || IP address || Yes || 200 | ||
|- | |||
POSIX TZ | | H323 gatekeeper id || String || No || 201 | ||
|- | |||
Default coder | | POSIX TZ || String || No || 202 | ||
|- | |||
Language | | Default coder || String || No || 203 | ||
|- | |||
Location | | Language || String || No || 204 | ||
|- | |||
VLAN ID2 | | Location || String || No || 205 | ||
|- | |||
VLAN Priority2 | | VLAN ID2 || Word (16bit) || No || 206 | ||
|- | |||
TOS Bits2 | | VLAN Priority2 || Byte (8bit) || No || 207 | ||
|- | |||
Enbloc dialling | | TOS Bits2 || String || No || 208 | ||
|- | |||
Dialtone type | | Enbloc dialling || Byte (8bit) || No || 209 | ||
|- | |||
Faststart | | Dialtone type || Byte (8bit) || No || 210 | ||
|- | |||
H245-Tunnelling | | Faststart || Byte (8bit) || No || 211 | ||
|- | |||
Clock type | | H245-Tunnelling || Byte (8bit) || No || 212 | ||
|- | |||
Static Routes | | Clock type || Byte (8bit) || No || 213 | ||
|- | |||
Update URL | | Static Routes || String || No || 214 | ||
|- | |||
Update Poll Interval | | Update URL || String || No || 215 | ||
|- | |||
LDAP directory | | Update Poll Interval || Word (16bit) || No || 216 | ||
|- | |||
| LDAP directory || String || No || 217 | |||
|} | |||
[[Image:How_to_use_the_innovaphone_DHCP_client_Dhcp4_conv.JPG]] | [[Image:How_to_use_the_innovaphone_DHCP_client_Dhcp4_conv.JPG]] | ||
| Line 185: | Line 173: | ||
===Configuration=== | ===Configuration=== | ||
To configure innovaphone vendor specific options for a specific scope, use the | To configure innovaphone vendor specific options for a specific scope, use the ''Configure options'' / ''Optionen konfigurieren'' entry in the scopes context menu. | ||
[[Image:DHow_to_use_the_innovaphone_DHCP_client_hcp5_conv.JPG]] | [[Image:DHow_to_use_the_innovaphone_DHCP_client_hcp5_conv.JPG]] | ||
| Line 201: | Line 189: | ||
The following table lists the available options and their meaning. | The following table lists the available options and their meaning. | ||
Option | {| border=1 | ||
|+ | |||
| Option || Meaning || How to code | |||
|- | |||
H323 gatekeeper | | H323 gatekeeper || Defines the IP address of both the primary and the alternate gatekeeper for the device. This is only required, if gatekeeper discovery is not feasible | ||
| | |||
This is an array of IP addresses. Put the primary gatekeepers IP into the first entry, the alternate gatekeepers IP into the second entry. Further entries are ignored. | |||
|- | |||
H323 gatekeeper id | | H323 gatekeeper id || The gatekeeper id of the gatekeeper the device likes to register with. Usually required only if several gatekeepers are running and a particular one must be chosen during gatekeeper discovery | ||
| | |||
Type the gatekeeper id as configured in the gateway or PBX configuration into the string field. | |||
|- | |||
POSIX TZ | | POSIX TZ || Defines both the time zone and the daylight saving time information. | ||
| | |||
Enter the correct TZ string into the string field as you would configure it in the devices configuration applet. See chapter 9.1.3 of the VoIP Gateways Version 5 manual. | |||
This option is in fact identical to the standard DHCP option number 88 (TZ). However, various DHCP servers do not support this option, so it is provided as a redundant vendor specific option. If your DHCP server supports option 88, the vendor specific option is not needed. | |||
|- | |||
| Default coder || Defines the preferred coder for H.245 coder negotiation, as well as the packet size when sending RTP packets and the use of CNG and VAD. | |||
| | |||
This string option must contain the value of the “/coder” option in the IP200’s configuration file, e.g. '''G729A,40,sec''' | |||
|- | |||
| Language || Defines the user interface language | |||
| | |||
This string must contain the value of the '''/lang''' option in the IP200’s configuration file, e.g. '''eng''' | |||
|- | |||
| Location || Defines the various PBX access numbers (country code etc.) for the device. | |||
| | |||
This string must contain the '''/cc''', '''/ac''', '''/ntp''', '''/itp''', '''/col''' and '''/pbx''' options in the IP200’s configuration file, e.g. '''/cc 49 /ac 7031 /ntp 0 /itp 00 /col 0 /pbx 7''' (althought, to save bytes, you may omit the '''/'''-es) | |||
|- | |||
| VLAN ID || The 802.1q VLAN ID for traffic sent and received by the device | |||
| | |||
Enter the numerical ID into the 16bit edit field | |||
|- | |||
| VLAN Priority || The 802.1p VLAN priority for traffic sent by the device | |||
| | |||
Enter the numerical priority into the 8bit edit field | |||
|- | |||
| TOS Bits || The value for the IP TOS field in the IP header of voice traffic sent by the device | |||
| | |||
Enter the numerical priority into the string field. You may prefix with '''0x''' to specify hexadecimal numbers (or '''0''' to specify octal numbers) | |||
|- | |||
| Enbloc Dialling || The number of seconds dialled digits are kept in the IP200 before they are sent en-bloc to the gatekeeper | |||
| | |||
Enter the number of seconds into the 8bit edit field. A value of '''0''' indicates that en-bloc dialling is turned off and digits are sent to the gatekeeper as they are dialled | |||
|- | |||
| Dialtone type || The type of dialtone to generate locally | |||
| | |||
Enter the numeric dialtone type (e.g. '''0''' - german PBX, '''1''' – german PSTN, '''2''' – US) | |||
|- | |||
| Faststart || Disable/Enable the H245 faststart procedure | |||
| | |||
To disable enter '''0''', otherwise enter '''1''' into the 8bit edit field | |||
|- | |||
| H245-Tunnelling || Disable/Enable H245 tunneling | |||
| | |||
To disable enter '''0''', otherwise enter '''1''' into the 8bit edit field | |||
|- | |||
| H245-Tunnelling || Define format of date and time display | |||
| | |||
Enter the numeric clock type ('''0''' – ''dd''.''mm''.''yy'' ''hh'':''mm'', 24 hour clock; '''1''' – ''mm''/''dd'' ''hh'':''mm'' ''xm'', 12 hour am/pm clock) | |||
|- | |||
| Static Routes || Static routes to be added to the routes already defined in the device configuration | |||
| | |||
The string (max 127 characters) must contain comma separated route definitions in the form ''address'':'''''mask''''':'''''gateway'' | |||
''address'', ''mask'' and ''gateway'' are expected in dotted decimal notation, mask (but not the colon) can be left off in a host route | |||
|- | |||
| Update URL || URL to retrieve update commands from. This is identical to the /url option parameter of the UP1 module | |||
| | |||
Complete URL as in '''http://192.168.0.10/file.txt'''. No symbolic host names are supported | |||
|- | |||
| Update poll interval || Standard poll interval in minutes. This is identical to the '''/poll''' option parameter of the UP1 module | |||
| | |||
Interval in minutes | |||
|- | |||
| LDAP directory || Defines the various Parameters required to access an LDAP directory | |||
|} | |||
===Determining option values with V6=== | |||
In V6 (from SR1), there is [[Howto:Valid_values_for_innovaphone_DHCP_verndor_options | a simple method avalable ]] to paste the values from a phones web GUI. | |||
===Determining LDAP options=== | |||
To determine a proper configuration for option 217 (LDAP), you best proceed as follows: | To determine a proper configuration for option 217 (LDAP), you best proceed as follows: | ||
*Take a phone and configure it with static IP address | |||
*Tweak the LDAP settings (''Registration 1 / Directories / Extern'') as desired | |||
*Look at '''http://''x.x.x.x''/!mod cmd PHONE DIR ldap-config''' | |||
*Set option 217 to the string shown | |||
===Disabling the DHCP client=== | |||
In certain circumstances, it is convenient to partly disable the DHCP client. This way, the device still gets its IP address from the DHCP server, however, additional settings possibly supplied by the DHCP server are ignored. This is especially useful if in a given setup, some devices are to be configured differently but the majority is still configured by DHCP. | |||
Disabling the DHCP client | |||
In certain circumstances, it is convenient to partly disable the DHCP client. This way, the device still gets its IP address from the DHCP server, however, additional settings possibly supplied by the DHCP server are ignored. This especially useful if in a given setup, some devices are to be configured differently but the majority is still configured by DHCP. | |||
This can be achieved using the following config file options | This can be achieved using the following config file options | ||
{| | |||
|'''config change UP1 /no-dhcp''' | |||
|the update server uses the config files configuration even though there is a configuration supplied from DHCP (innovaphone vendor options "Update URL [215]" and "Update Poll Interval [216]" are ignored). | |||
|- | |||
|'''config change DHCPn /no-vlan''' | |||
|the VLAN settings use the config files configuration even though there is a configuration supplied from DHCP (innovaphone vendor options "VLAN ID [206]" and "VLAN Priority [207]" are ignored)... | |||
|- | |||
|'''config change DHCPn /no-vendor''' | |||
|all innovaphone vendor options are ignored. | |||
|} | |||
===Known Problems with lengthy options=== | |||
The minimum space available for options in a BOOTP/DHCP record is 312 byte. There are some extension mechanisms but only a few DHCP servers support it. The Windows 2000 DHCP server for example does not, but silently truncates options not fitting in this 312 byte space. Thus it’s nearly impossible to distribute the LDAP directory configuration with a Windows 2000 server but it’s no problem with the DHCP Server built into each innovaphone device. | |||
===Known Problems with VLAN Configurations=== | |||
Known Problems with VLAN Configurations | |||
The handling of the 802.1q VLAN ID is a bit tricky. If not hard configured otherwise, the IP200 will request a DHCP lease using the Ethernet switch ports default VLAN ID (that is, it will not send any VLAN header). It will thus receive a DHCP offer dedicated to devices on that VLAN. If this offer includes a VLAN ID option, the IP200 will not accept the offered lease, set the VLAN ID to the value received in the otherwise disregarded offer and start the DHCP process all over again. Now, the DHCP request will be issued on a new VLAN ID. Therefore, the DHCP server will now send an offer dedicated for devices on that new VLAN. This will most probably be a different DHCP scope. | The handling of the 802.1q VLAN ID is a bit tricky. If not hard configured otherwise, the IP200 will request a DHCP lease using the Ethernet switch ports default VLAN ID (that is, it will not send any VLAN header). It will thus receive a DHCP offer dedicated to devices on that VLAN. If this offer includes a VLAN ID option, the IP200 will not accept the offered lease, set the VLAN ID to the value received in the otherwise disregarded offer and start the DHCP process all over again. Now, the DHCP request will be issued on a new VLAN ID. Therefore, the DHCP server will now send an offer dedicated for devices on that new VLAN. This will most probably be a different DHCP scope. | ||
| Line 349: | Line 314: | ||
First Boot | *First Boot | ||
The client will broadcast a DHCP DISCOVER, expecting an OFFER from the server including all requested parameters. If the client intends to use the offered lease, it will issue a request for the offered lease. Once it receives an ACK for the lease requested, it will configure itself accordingly. All lease information is stored in the devices config file using the /laddr option (unless suppressed using /no-keep). | The client will broadcast a DHCP DISCOVER, expecting an OFFER from the server including all requested parameters. If the client intends to use the offered lease, it will issue a request for the offered lease. Once it receives an ACK for the lease requested, it will configure itself accordingly. All lease information is stored in the devices config file using the /laddr option (unless suppressed using /no-keep). | ||
Re-boot | *Re-boot | ||
If there is lease information (in the /laddr config file option), the client will broadcast requests for the same lease again. If there is no answer within 30 seconds, the device will configure itself using the parameters in /laddr. It will nevertheless continue to request this lease from the DHCP server again (every 30 seconds, a broadcast will be sent). | If there is lease information (in the /laddr config file option), the client will broadcast requests for the same lease again. If there is no answer within 30 seconds, the device will configure itself using the parameters in /laddr. It will nevertheless continue to request this lease from the DHCP server again (every 30 seconds, a broadcast will be sent). | ||
| Line 364: | Line 327: | ||
*First boot with VLAN ID option received | |||
First boot with VLAN ID option received | |||
If an offered lease includes the VLAN-ID option and the ID proposed differs from the VLAN ID the devices currently operates with (that is, from the id configured in the devices configuration), the device will change its VLAN ID to the one received in the VLAN-ID option. It will not request the lease though. Instead, it will continue to send DISCOVER requests on the new VLAN ID. If a lease is obtained there, all lease information is stored in the config file as usual. | If an offered lease includes the VLAN-ID option and the ID proposed differs from the VLAN ID the devices currently operates with (that is, from the id configured in the devices configuration), the device will change its VLAN ID to the one received in the VLAN-ID option. It will not request the lease though. Instead, it will continue to send DISCOVER requests on the new VLAN ID. If a lease is obtained there, all lease information is stored in the config file as usual. | ||
You can disable the VLAN-ID processing using the /no-vlan option. | You can disable the VLAN-ID processing using the '''/no-vlan''' option. | ||
Reboot with VLAN ID | *Reboot with VLAN ID | ||
If the device finds lease information in the config file at boot time and if there is a VLAN ID different from the devices current VLAN-ID, it will re-configure itself to the new VLAN ID and try to request the saved lease as usual. If the lease is rejected with a NAK by the server, the device will re-configure itself to the pre-configured VLAN ID and try to DISCOVER a new lease as usual. | If the device finds lease information in the config file at boot time and if there is a VLAN ID different from the devices current VLAN-ID, it will re-configure itself to the new VLAN ID and try to request the saved lease as usual. If the lease is rejected with a NAK by the server, the device will re-configure itself to the pre-configured VLAN ID and try to DISCOVER a new lease as usual. | ||
| Line 379: | Line 341: | ||
Changing configuration options set by DHCP options | ===Changing configuration options set by DHCP options=== | ||
If a device has been configured by DHCP, you cannot change those parameters. Any attempt to do so will issue a “Reset required” message. | If a device has been configured by DHCP, you cannot change those parameters. Any attempt to do so will issue a “Reset required” message. | ||
| Line 388: | Line 350: | ||
[1] This option is in fact identical to the standard DHCP option number 88 (TZ). However, various DHCP servers do not support this option, so it is provided as a redundant vendor specific option. If your DHCP server supports option 88, the vendor specific option is not needed. | [1] This option is in fact identical to the standard DHCP option number 88 (TZ). However, various DHCP servers do not support this option, so it is provided as a redundant vendor specific option. If your DHCP server supports option 88, the vendor specific option is not needed. | ||
[[Category:Howto|{{PAGENAME}}]] | [[Category:Howto|{{PAGENAME}}]] | ||
Revision as of 14:52, 24 May 2007
innovaphone devices include a DHCP client which allows the IP interface to be configured from a DHCP server.
In addition to that, telephone devices allow configuring a number of settings via special DHCP vendor options.
Here is how the DHCP client works.
[ This article has been converted from the previous "howto" document in the V5 predoc folder and is intended to replace this ]
Applies To
This information applies to
- All innovaphone devices,
V5.01 Build 04-5679 and V6
More Information
Problem Details
The innovaphone devices do support auto configuration via standard DHCP options.
They additionally support some innovaphone vendor specific options to effect some VoIP specific configuration.
Some of them are generic; some of them are specific to the IP200.
These configurations include
| H323 Gatekeeper | The IP addresses of the main and alternate gatekeeper. IP200 only |
| H323 Gatekeeper ID | The ID of the gatekeeper taking care of the device. IP200 only |
| POSIX Time zone | The time zone string defining the time zone the device lives in (see the VoIP Gateways 5.0 Manual, chapter 9.1.3 for more details about time zone settings) |
| Default coder | The coder the device will try negotiate during media stream setup. IP200 only |
| Language | The user interface language of the device. IP200 only |
| Location | The location information (country code, area code etc.). IP200 only |
| VLAN ID | The VLAN ID for voice traffic |
| VLAN Priority | The VLAN Priority for voice traffic |
| TOS Bits | The value for the IP TOS field in the IP header of voice traffic |
| Enbloc dialling | Overlapped sending disabled. IP200 only |
| Dialtone type | The type of locally generated dial tones. IP200 only |
| Faststart | Disable/Enable the H245 faststart procedure |
| H245-Tunnelling | Disable/Enable H245 tunneling |
| Clock type | Format of date and time display. IP200 only |
| Static routes | Additional static routes |
| Configuration parameters for the update server | URL to retrieve update commands from and poll interval |
| LDAP directory configuration | Parameters to access an external LDAP directory. IP200 only |
System Requirements
To use vendor specific DHCP options, a DHCP server that supports such options is required.
Most popular DHCP server implementations such as the Microsoft Windows DHCP service and the Linux dhcpd do so.
Installation
For the DHCP server to support vendor specific options, the options must be made known to the server.
Consult the accompanying documentation which comes with your DHCP server implementation how to do this.
In this section, the installation of innovaphone vendor options is demonstrated using a Microsoft Windows 2000 DHCP server.
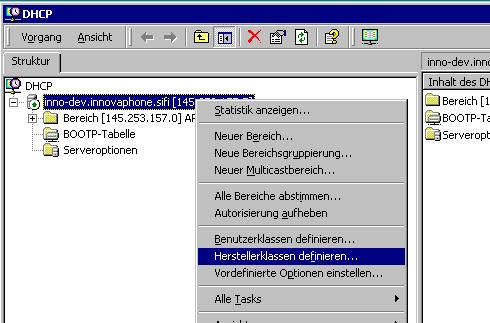
First you need to create a new vendor class.
Use the Define Vendor Class… / Herstellerklasse definieren menu entry on the DHCP server’s context menu
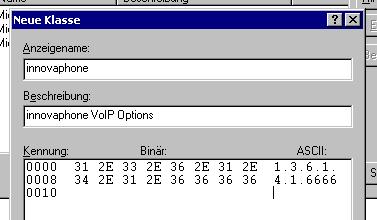
Add a new vendor class as follows:
| Anzeigename / Display name | innovaphone |
| Beschreibung / Description | innovaphone VoIP Options |
| Kennung / ID | (ASCII) 1.3.6.1.4.1.6666 |
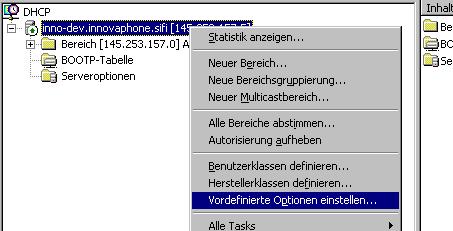
Add the innovaphone options. Use the Configure predefined options / Vordefinierte Optionen einstellen entry in the DHCP server’s context menu
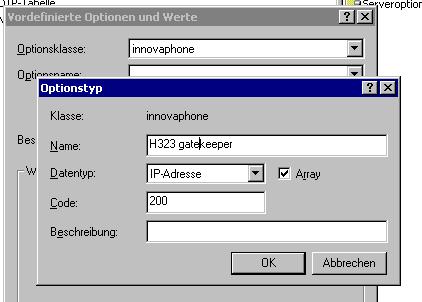
Select the innovaphone option class and add the innovaphone specific options
| Name | Data type | Array | Code |
| H323 gatekeeper | IP address | Yes | 200 |
| H323 gatekeeper id | String | No | 201 |
| POSIX TZ | String | No | 202 |
| Default coder | String | No | 203 |
| Language | String | No | 204 |
| Location | String | No | 205 |
| VLAN ID2 | Word (16bit) | No | 206 |
| VLAN Priority2 | Byte (8bit) | No | 207 |
| TOS Bits2 | String | No | 208 |
| Enbloc dialling | Byte (8bit) | No | 209 |
| Dialtone type | Byte (8bit) | No | 210 |
| Faststart | Byte (8bit) | No | 211 |
| H245-Tunnelling | Byte (8bit) | No | 212 |
| Clock type | Byte (8bit) | No | 213 |
| Static Routes | String | No | 214 |
| Update URL | String | No | 215 |
| Update Poll Interval | Word (16bit) | No | 216 |
| LDAP directory | String | No | 217 |
Configuration
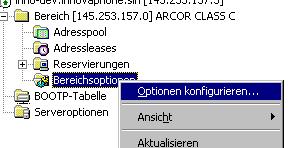
To configure innovaphone vendor specific options for a specific scope, use the Configure options / Optionen konfigurieren entry in the scopes context menu.
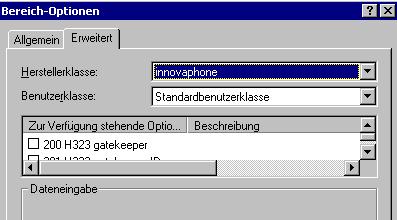
Select innovaphone in the Advanced / Erweitert tab sheet.
Tick the options you want to provide and edit the respective values.
The following table lists the available options and their meaning.
| Option | Meaning | How to code |
| H323 gatekeeper | Defines the IP address of both the primary and the alternate gatekeeper for the device. This is only required, if gatekeeper discovery is not feasible |
This is an array of IP addresses. Put the primary gatekeepers IP into the first entry, the alternate gatekeepers IP into the second entry. Further entries are ignored. |
| H323 gatekeeper id | The gatekeeper id of the gatekeeper the device likes to register with. Usually required only if several gatekeepers are running and a particular one must be chosen during gatekeeper discovery |
Type the gatekeeper id as configured in the gateway or PBX configuration into the string field. |
| POSIX TZ | Defines both the time zone and the daylight saving time information. |
Enter the correct TZ string into the string field as you would configure it in the devices configuration applet. See chapter 9.1.3 of the VoIP Gateways Version 5 manual. This option is in fact identical to the standard DHCP option number 88 (TZ). However, various DHCP servers do not support this option, so it is provided as a redundant vendor specific option. If your DHCP server supports option 88, the vendor specific option is not needed. |
| Default coder | Defines the preferred coder for H.245 coder negotiation, as well as the packet size when sending RTP packets and the use of CNG and VAD. |
This string option must contain the value of the “/coder” option in the IP200’s configuration file, e.g. G729A,40,sec |
| Language | Defines the user interface language |
This string must contain the value of the /lang option in the IP200’s configuration file, e.g. eng |
| Location | Defines the various PBX access numbers (country code etc.) for the device. |
This string must contain the /cc, /ac, /ntp, /itp, /col and /pbx options in the IP200’s configuration file, e.g. /cc 49 /ac 7031 /ntp 0 /itp 00 /col 0 /pbx 7 (althought, to save bytes, you may omit the /-es) |
| VLAN ID | The 802.1q VLAN ID for traffic sent and received by the device |
Enter the numerical ID into the 16bit edit field |
| VLAN Priority | The 802.1p VLAN priority for traffic sent by the device |
Enter the numerical priority into the 8bit edit field |
| TOS Bits | The value for the IP TOS field in the IP header of voice traffic sent by the device |
Enter the numerical priority into the string field. You may prefix with 0x to specify hexadecimal numbers (or 0 to specify octal numbers) |
| Enbloc Dialling | The number of seconds dialled digits are kept in the IP200 before they are sent en-bloc to the gatekeeper |
Enter the number of seconds into the 8bit edit field. A value of 0 indicates that en-bloc dialling is turned off and digits are sent to the gatekeeper as they are dialled |
| Dialtone type | The type of dialtone to generate locally |
Enter the numeric dialtone type (e.g. 0 - german PBX, 1 – german PSTN, 2 – US) |
| Faststart | Disable/Enable the H245 faststart procedure |
To disable enter 0, otherwise enter 1 into the 8bit edit field |
| H245-Tunnelling | Disable/Enable H245 tunneling |
To disable enter 0, otherwise enter 1 into the 8bit edit field |
| H245-Tunnelling | Define format of date and time display |
Enter the numeric clock type (0 – dd.mm.yy hh:mm, 24 hour clock; 1 – mm/dd hh:mm xm, 12 hour am/pm clock) |
| Static Routes | Static routes to be added to the routes already defined in the device configuration |
The string (max 127 characters) must contain comma separated route definitions in the form address:mask:gateway address, mask and gateway are expected in dotted decimal notation, mask (but not the colon) can be left off in a host route |
| Update URL | URL to retrieve update commands from. This is identical to the /url option parameter of the UP1 module |
Complete URL as in http://192.168.0.10/file.txt. No symbolic host names are supported |
| Update poll interval | Standard poll interval in minutes. This is identical to the /poll option parameter of the UP1 module |
Interval in minutes |
| LDAP directory | Defines the various Parameters required to access an LDAP directory |
Determining option values with V6
In V6 (from SR1), there is a simple method avalable to paste the values from a phones web GUI.
Determining LDAP options
To determine a proper configuration for option 217 (LDAP), you best proceed as follows:
- Take a phone and configure it with static IP address
- Tweak the LDAP settings (Registration 1 / Directories / Extern) as desired
- Look at http://x.x.x.x/!mod cmd PHONE DIR ldap-config
- Set option 217 to the string shown
Disabling the DHCP client
In certain circumstances, it is convenient to partly disable the DHCP client. This way, the device still gets its IP address from the DHCP server, however, additional settings possibly supplied by the DHCP server are ignored. This is especially useful if in a given setup, some devices are to be configured differently but the majority is still configured by DHCP.
This can be achieved using the following config file options
| config change UP1 /no-dhcp | the update server uses the config files configuration even though there is a configuration supplied from DHCP (innovaphone vendor options "Update URL [215]" and "Update Poll Interval [216]" are ignored). |
| config change DHCPn /no-vlan | the VLAN settings use the config files configuration even though there is a configuration supplied from DHCP (innovaphone vendor options "VLAN ID [206]" and "VLAN Priority [207]" are ignored)... |
| config change DHCPn /no-vendor | all innovaphone vendor options are ignored. |
Known Problems with lengthy options
The minimum space available for options in a BOOTP/DHCP record is 312 byte. There are some extension mechanisms but only a few DHCP servers support it. The Windows 2000 DHCP server for example does not, but silently truncates options not fitting in this 312 byte space. Thus it’s nearly impossible to distribute the LDAP directory configuration with a Windows 2000 server but it’s no problem with the DHCP Server built into each innovaphone device.
Known Problems with VLAN Configurations
The handling of the 802.1q VLAN ID is a bit tricky. If not hard configured otherwise, the IP200 will request a DHCP lease using the Ethernet switch ports default VLAN ID (that is, it will not send any VLAN header). It will thus receive a DHCP offer dedicated to devices on that VLAN. If this offer includes a VLAN ID option, the IP200 will not accept the offered lease, set the VLAN ID to the value received in the otherwise disregarded offer and start the DHCP process all over again. Now, the DHCP request will be issued on a new VLAN ID. Therefore, the DHCP server will now send an offer dedicated for devices on that new VLAN. This will most probably be a different DHCP scope.
As a consequence, DHCP options of IP200’s on a non-default VLAN must be configured twice. The VLAN ID option itself must be configured in the default VLANs DHCP scope. All other options must be configured in the new VLANs DHCP scope.
Be sure to configure the VLAN in both scopes identically. If not, the DHCP client process will never terminate, since it will always detect a changed VLAN ID, set the VLAN ID and restart the DHCP process.
Here is how DHCP leases are handled in detail:
- First Boot
The client will broadcast a DHCP DISCOVER, expecting an OFFER from the server including all requested parameters. If the client intends to use the offered lease, it will issue a request for the offered lease. Once it receives an ACK for the lease requested, it will configure itself accordingly. All lease information is stored in the devices config file using the /laddr option (unless suppressed using /no-keep).
- Re-boot
If there is lease information (in the /laddr config file option), the client will broadcast requests for the same lease again. If there is no answer within 30 seconds, the device will configure itself using the parameters in /laddr. It will nevertheless continue to request this lease from the DHCP server again (every 30 seconds, a broadcast will be sent).
If the server acknowledges the old lease, the client will check for changes in the DHCP options and re-configure itself accordingly. Changed options will be saved in the config file.
If the server rejects the lease using a NAK, the client will forget about the lease and continue to operate like it does for the first boot.
- First boot with VLAN ID option received
If an offered lease includes the VLAN-ID option and the ID proposed differs from the VLAN ID the devices currently operates with (that is, from the id configured in the devices configuration), the device will change its VLAN ID to the one received in the VLAN-ID option. It will not request the lease though. Instead, it will continue to send DISCOVER requests on the new VLAN ID. If a lease is obtained there, all lease information is stored in the config file as usual.
You can disable the VLAN-ID processing using the /no-vlan option.
- Reboot with VLAN ID
If the device finds lease information in the config file at boot time and if there is a VLAN ID different from the devices current VLAN-ID, it will re-configure itself to the new VLAN ID and try to request the saved lease as usual. If the lease is rejected with a NAK by the server, the device will re-configure itself to the pre-configured VLAN ID and try to DISCOVER a new lease as usual.
Changing configuration options set by DHCP options
If a device has been configured by DHCP, you cannot change those parameters. Any attempt to do so will issue a “Reset required” message.
[1] This option is in fact identical to the standard DHCP option number 88 (TZ). However, various DHCP servers do not support this option, so it is provided as a redundant vendor specific option. If your DHCP server supports option 88, the vendor specific option is not needed.