Howto:How to Connect to a VoIP Provider: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==Gateway Interfaces== | ==Gateway Interfaces== | ||
Most of the VoIP providers require a registration to make and receive calls. | Most of the VoIP providers require a registration to make and receive calls. | ||
* Select one of the four SIP interfaces (Gateway/Interfaces) | |||
* Give it a descriptive name into '''Name''' (e.g. "sipgate.de") | ===External Registration at the SIP provider=== | ||
* Enter you registration ID into '''ID''' (e.g. "1234567") | * Select one of the four SIP interfaces (Gateway/Interfaces). | ||
* Enter the SIP provider's domain name into right side of '''@''' (e.g. "sipgate.de") | * Give it a descriptive name into '''Name''' (e.g. "sipgate.de"). | ||
* If the SIP provider's domain name cannot be resolved into an IP address by DNS, you must enter the provider's IP address manually into '''Server Address (primary)''' | * Enter you registration ID into '''ID''' (e.g. "1234567"). | ||
* Enter the SIP provider's domain name into right side of '''@''' (e.g. "sipgate.de"). | |||
* If the SIP provider's domain name cannot be resolved into an IP address by DNS, you must enter the provider's IP address manually into '''Server Address (primary)'''. | |||
* If authorization is required by the SIP provider, enter the username and password into '''Username''' and '''Password'''. In most cases the authentication username is identical to the registration ID. | * If authorization is required by the SIP provider, enter the username and password into '''Username''' and '''Password'''. In most cases the authentication username is identical to the registration ID. | ||
* Depending on whether your Gateway device has a local public IP address, you must configure a '''STUN server''' in order to setup voice calls with the SIP provider. | |||
Example: [[Image:Sip_config.jpg]] | Example: [[Image:Sip_config.jpg]] | ||
===Internal Registration at the innovaphone PBX=== | |||
==NAT Problems== | ==NAT Problems== | ||
Revision as of 11:13, 11 September 2007
Work in progress!
Abstract
This document is intended to help you to connect your innovaphone PBX to a VoIP provider.
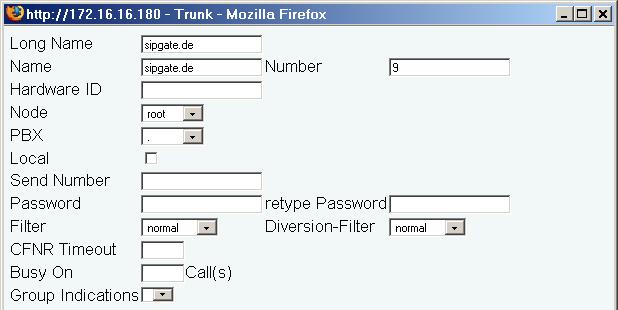
PBX Trunk Object
Add a trunk object to your PBX. Assign a trunk prefix and a talking name (e.g. "sipgate.de").
Gateway Interfaces
Most of the VoIP providers require a registration to make and receive calls.
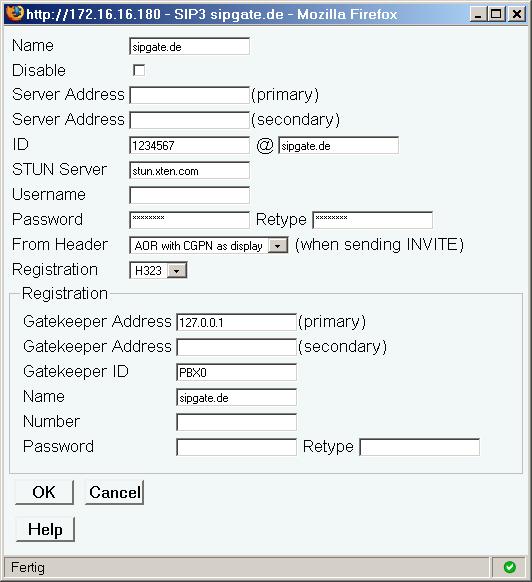
External Registration at the SIP provider
- Select one of the four SIP interfaces (Gateway/Interfaces).
- Give it a descriptive name into Name (e.g. "sipgate.de").
- Enter you registration ID into ID (e.g. "1234567").
- Enter the SIP provider's domain name into right side of @ (e.g. "sipgate.de").
- If the SIP provider's domain name cannot be resolved into an IP address by DNS, you must enter the provider's IP address manually into Server Address (primary).
- If authorization is required by the SIP provider, enter the username and password into Username and Password. In most cases the authentication username is identical to the registration ID.
- Depending on whether your Gateway device has a local public IP address, you must configure a STUN server in order to setup voice calls with the SIP provider.
Internal Registration at the innovaphone PBX
NAT Problems
By default the Gateway is working in transit mode. This means RTP addresses are going to be exchanged between the communication endpoints. If calls are established between an internal endpoint (with private IP address) and the VoIP provider (with public IP address) the private RTP address of the internal endpoint will be passed-through to the VoIP provider.
A VoIP provider cannot send to private RTP addresses!
A media relay mode has been implemented to get RTP working in this scenario. In media relay mode the Gateway does not pass-through private RTP addresses to the VoIP provider. It allocates local RTP ports instead and forwards RTP between the internal and the external endpoint.
If the Gateway itself does not have a public IP address (check your IP configuration), it still will announce a private RTP address to the VoIP provider even in media relay mode. In this case you must use a STUN server to create NAT mappings at your local NAT router. Using a STUN server is not necessary if your Gateway has a public local IP address.
The Gateway and the PBX will automatically work in media relay mode on connections between private and non-private endpoints. You must declare all private IP addresses (Reference:Configuration/IP/Settings). If no private IP addresses are declared (default) all IP addresses will be interpreted as public (non-private) by the Gateway/PBX and transit mode will be applied.
Diagnostics
Registration Problems
To do ...
Signaling Problems
To do ...
Media Problems
Setup a call between an internal endpoint and the VoIP provider.
Check the call views of Gateway and PBX while the call is connected.
The Gateway should work in media relay mode ("RELAY").
The PBX should work in transit mode ("TRANSIT").