Howto:Mobility GSM Client for Windows Mobile: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The GSM | The ''GSM Client'' software is used for easy access to the mobility | ||
functions of V8 PBX from Windows Mobile phones. The ''GSM Client'' software | |||
is provided as a part of the ''gsm'' package | |||
which can be used to prepare Client configuration for transfer on the | |||
mobile device. | |||
==Applies To== | ==Applies To== | ||
This information applies to | This information applies to | ||
*innovaphone PBX V8 | *innovaphone PBX V8 hotfix6, Build 8050020 or later | ||
*innovaphone | *innovaphone ''gsm'' Package, Build 1045 or later | ||
==More Information== | ==More Information== | ||
===Requirements=== | |||
== | === On the Administrator's PC === | ||
*Operating System Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 or later | |||
*.Net Framework 3.5 | |||
*ActiveSync 4.5 or later | |||
* [http://download.innovaphone.com/ice/8.00/#gsm Firmware V8-based GSM Phone Client RC1 or later] | |||
==== On the Mobile Phone ==== | |||
The ''GSM Client'' software requires a Windows Mobile device. Create a backup of mobile device, before installing beta software! | |||
*Windows Mobile 5.x, 6.x | |||
*Smart Phone or Pocket PC | |||
*CF 2.0 SP2 installed | |||
*Internet Access (optional) | |||
==== On the PBX ==== | |||
* [http://download.innovaphone.com/ice/8.00/#firmware Firmware V8 hotfix6 or later] | |||
* ''GSM-1'' Client Licenses installed | |||
* ''Mobility-8'' Licenses installed | |||
=== | === Overview === | ||
The ''GSM Client'' is an application that needs to be installed on the | |||
mobile phone. It replaces the standard phone application with a | |||
dedicated interface which converts the mobile phone in to a PBX | |||
Extension. | |||
While this allows the client to provide PBX features in a useful way, it | |||
also has the drawback that the native phone application is no longer | |||
available. If this is not acceptable, there are other solutions | |||
available in the market which do not replace the native phone client, | |||
but add some functionality to it (cf. | |||
[[Howto:OptiCaller_Client_-_OptiCaller_AB_-_3rd_Party_Product | OptiCaller]] | |||
as an example). By design, such clients cannot offer the | |||
same functionality though. | |||
The client assumes the existence and a specific configuration of the | |||
mobility functions in the PBX. It is therefore necessary to do the | |||
appropriate configuration on the PBX in order to use the ''GSM Client'' | |||
This configuration must be done using the PBX's standard administration | |||
facilities. | |||
The ''GSM Client'' requires proper configuration to make the individual | |||
system characteristics (trunk lines, extensions ...) known to it. This | |||
configuration can be created automatically from the PBX data using the | |||
''GSM-Client Configuration File Creator''. This is a stand-alone PC | |||
application. It is intended to be used by the mobile phone | |||
administrator, end users will not need to work with the tool. The | |||
resulting configuration files are then transferred to the mobile phones | |||
using standard mechanisms provided by the phone's operating system (e.g. | |||
ActiveSync). The ''GSM-Client Configuration File Creator'' also greatly | |||
simplifies use of these mechanisms. | |||
[[ | Once rollout to the mobile phone is done, configuration files have to be | ||
updated on the phones only rarely (e.g. if the trunk access changes). | |||
However, the PBX's extension list, which is also provided to the phone | |||
will obviously change more frequently. A mechanism to roll-out updates | |||
to this list is provided therefore. | |||
The roll-out process for the ''GSM Client'' looks as follows thus | |||
General preparation: | |||
# download the latest ''gsm'' package from innovaphone's [http://download.innovaphone.com/ice/8.00/#gsm download page]. It includes both the ''GSM-Client Configuration File Creator'' and the ''GSM Client'' for the platforms supported (currently Windows Mobile Smartphone and Windows Mobile PocketPC) | |||
# install this package on the administrator's PC | |||
# obtain and install mobility and gsm client licenses | |||
# provide proper mobility objects configuration on the PBX | |||
When this is done, rollout to the individual phones requires the following steps per phone | |||
# add the individual mobile phone information to the user objects | |||
# (re-)create ''GSM Client'' configuration files using the ''GSM-Client Configuration File Creator'' | |||
# install the ''GSM Client'' program on the mobile phone | |||
# install the configuration files created ion the second step on the mobile phone | |||
When the extension list has changed on the PBX, the following steps are required to update the mobile phones | |||
# (re-)create ''GSM Client'' configuration files using the ''GSM-Client Configuration File Creator'' | |||
# install the extension file created on the previous step on the mobile phone | |||
All mobile phones share the same set of configuration files, so it is not necessary to create separate configurations for each individual phone. | |||
=== PBX Configuration === | |||
The following configurations must be done on the PBX | |||
* Creation of the [[Reference8:Administration/PBX/Objects/Mobility |mobility objects]] | |||
* Creation of the [[Reference8:Administration/PBX/Objects/DTMF_Features | DTMF features objects ]] | |||
* Attribution of the respective [[Reference8:Administration/PBX/Objects/Trunk_Line | trunk line objects ]] | |||
* Installation of proper GSM-1 and Mobility-8 licenses | |||
* Attribution of the respective [[Reference8:Administration/PBX/Objects/Edit_Forks | user forking entries ]] | |||
==== Numbering Plan ==== | |||
Mobility is based on a number of feature codes which are used by the | |||
mobile phone to access the features. These codes are in fact objects in | |||
the PBX (Mobility and DTMF-Feature) which need to be called. As a | |||
result, these feature codes each require individual extensions in the | |||
PBX's numbering plan. To make things worse, the GSM network does not | |||
carry * or # digits in a called number, so the extensions to be used | |||
must be plain numbers. | |||
You will need to reserve a number of extensions with a common prefix | |||
thus in your PBX's numbering plan. If this is not possible (e.g. | |||
because you reside in a country with a fixed numbering plan and you | |||
don't have a block large enough to allocate the numbers), you may | |||
revert to use a single extension in your numbering plan. Be aware | |||
though that this will result in | |||
* cost charged by your mobile operator for invoking features (some of the features are normally invoked by calling an extension without accepting the call, which should be free. When using a single extension, all features are invoked by calling this number, accepting the call and then dialling the desired feature using in-band DTMF tones) | |||
* longer execution time for most of the features invoked | |||
You need thus determine an available prefix for the feature codes within you PBX's numbering plan (say <code>54</code>). | |||
For the remainder of this article, we will refer to this prefix as ''mobility-prefix''. | |||
==== Mobility Object ==== | |||
There must be a mobility object on each PBX system with a mobility | |||
enabled user (that is, a user with an integrated mobile phone). The | |||
easiest way to achieve this is to create a mobility object with ''Node'' | |||
and ''PBX'' left empty. | |||
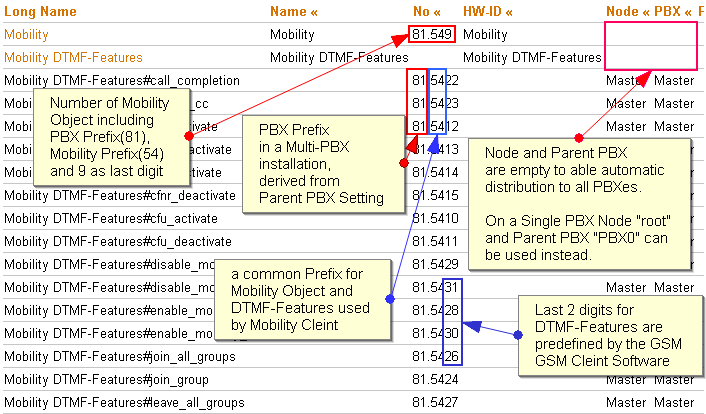
The ''Number'' property of the mobility object must be set to the ''mobility-prefix'' chosen plus literal <code>9</code>. | |||
This will result in one mobility object per PBX which has the PBX's node number as a prefix. Assuming the PBX's node number is <code>81</code>, the full number of the mobility object in our example would be <code>81549</code>. | |||
[[Image: | [[Image:Mobility Prefix 01.png]] | ||
The | ==== DTMF-Features Object ==== | ||
Again, there must be a DTMF-Features object on each PBX system with a mobility | |||
enabled user (that is, a user with an integrated mobile phone). The | |||
easiest way to achieve this is to create a DTMF-Features object with ''Node'' | |||
and ''PBX'' left empty. | |||
The DTMF-Features object itself does not have a ''Number'' property. Instead, the individual features have one. The features must have fixed numbers according to the following table: | |||
{| | {| | ||
| CFU Activate || | | CFU Activate || ''mobility-prefix''<code>10$#</code> || Deactivate || ''mobility-prefix''<code>11</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| CFB Activate || | | CFB Activate || ''mobility-prefix''<code>12$#</code> || Deactivate || ''mobility-prefix''<code>13</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| CFNR Activate || | | CFNR Activate || ''mobility-prefix''<code>14$#</code> || Deactivate || ''mobility-prefix''<code>15</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Pickup Group || | | Pickup Group || ''mobility-prefix''<code>16</code> || Directed || ''mobility-prefix''<code>17$#</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Park || | | Park || ''mobility-prefix''<code>18$</code> || Unpark || ''mobility-prefix''<code>19$</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Park To || | | Park To || ''mobility-prefix''<code>20$(1)$#</code> || Unpark From || ''mobility-prefix''<code>21$(1)$#</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Call Completion Busy || | | Call Completion Busy || ''mobility-prefix''<code>22$#</code> || Cancel || ''mobility-prefix''<code>23$#</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Join Group || | | Join Group || ''mobility-prefix''<code>24$#</code> || Leave || ''mobility-prefix''<code>25$#</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Join All Groups || | | Join All Groups || ''mobility-prefix''<code>26</code> || Leave || ''mobility-prefix''<code>27</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Enable mobility || | | Enable mobility || ''mobility-prefix''<code>28</code> || Disable mobility || ''mobility-prefix''<code>29</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Enable mobility cw || | | Enable mobility cw || ''mobility-prefix''<code>30</code> || Disable mobility cw || ''mobility-prefix''<code>31</code> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Set presence || | | Set presence || ''mobility-prefix''<code>32$(1)$(1)</code> || Unset presence || ''mobility-prefix''<code>33$(1)</code> | ||
|} | |} | ||
In our example, the list of mobility related objects should look like this: | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
DTMF-Features#call_completion 81.5422 | DTMF-Features#call_completion 81.5422 | ||
| Line 107: | Line 198: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
==== Trunk Lines ==== | |||
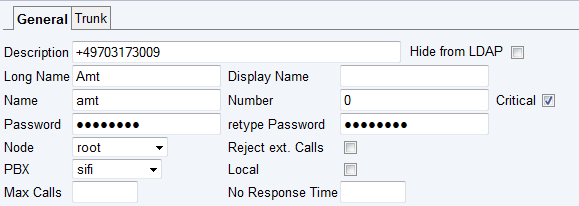
You do not need to create new trunk line objects for mobility. Instead, you need to attribute the existing objects to make their E.164 number known to the system. | |||
For this, you need to edit each trunk line and put the lines international number into its ''Description'' property. This must be done using the international number format, starting with <code>+</code>. Assuming the trunk line in our example has subscriber number <code>73009</code>, area code <code>7031</code> and county code <code>49</code>, you would specify <code>+49703173009</code>. Do not add your switchboard extension (usually <code>0</code> here!). | |||
[[Image:Howto-Mobility_GSM_Client_for_Windows_Mobile_Trunk_gsm.png]] | |||
==== Users ==== | |||
To enable mobility for a user, you need to | |||
* make sure you have both ''Mobility-8'' and ''GSM-1'' licenses available. As usual, test licenses are available from within [http://my.innovaphone.com my.innovaphone] | |||
* add a forking destination for each mobile phone the user wants to use with mobility | |||
* make the users mobile phone numbers known to the system | |||
* make the users mobile phone IMEI known to the system | |||
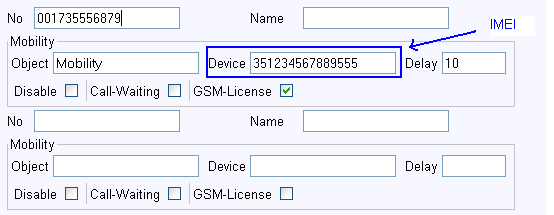
Put the phone's number into the ''No'' property. This number must be | |||
specified exactly as it would be received by the PBX when this phone | |||
calls in. That is, it is the number including GSM carrier prefix and | |||
trunk prefix, no country code, no <code>+</code>. Assuming the users | |||
mobile number is <code>017247110815</code> and the trunk line prefix in | |||
your PBX is <code>0</code>, you would specify | |||
<code>0017247110815</code>. | |||
Put the phone's IMEI into the ''Device'' property of the respective | |||
forking entry. The IMEI will always be a 15-digit number, such as e.g. | |||
<code>354503021446625</code>. If your IMEI is 17-digits instead, leave | |||
out the last 2 digits simply. In Windows Mobile, you can find the | |||
device's IMEI number in the ''Settings/System/Device Information'' | |||
(''Einstellungen/System/Geräte-Information''). The IMEI may also be | |||
display by dialling <code>*#06#</code> from within the phone's native | |||
phone application. | |||
Make sure the ''GSM-License'' check mark is ticked for the respective forking entry! | |||
[[Image:Mobility_GSM_Client_for_Windows_Mobile_1.png]] | |||
=== Configuration Generation === | |||
Download the ''gsm'' package from innovaphone's [http://download.innovaphone.com/ice/8.00/#gsm download page]. Install <code>pcsetup.msi</code> and follow the instructions in ''Start/Applications/innovaphone/GSM Client/Readme''. | |||
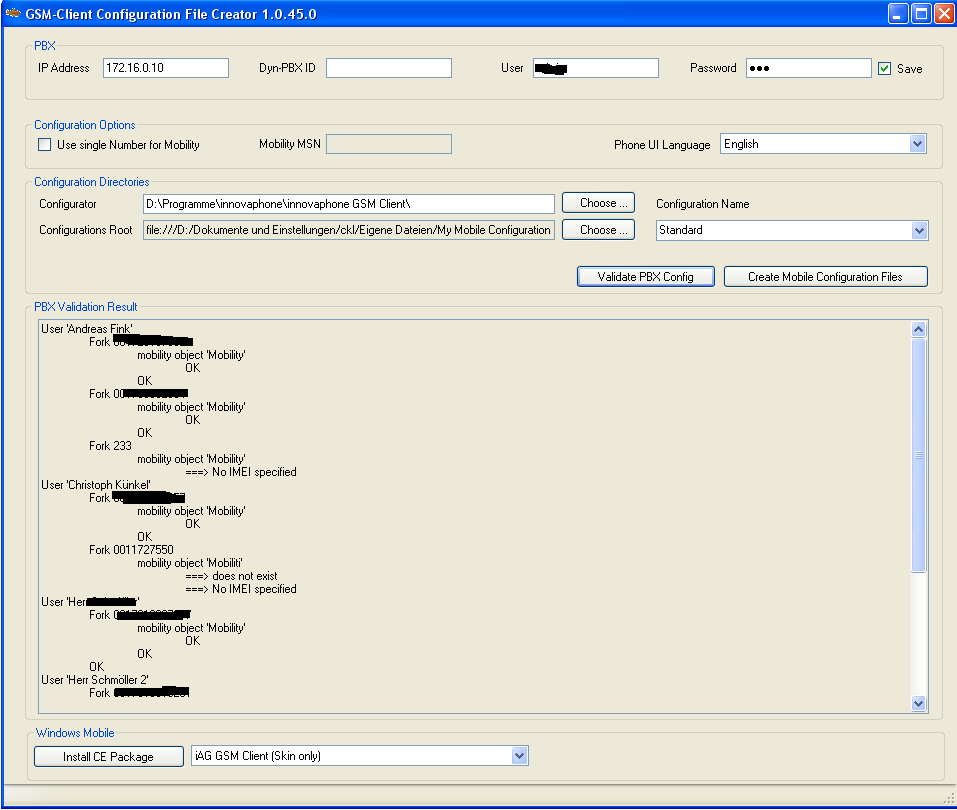
The ''GSM Client'' configuration files can be generated using the ''GSM-Client Configuration File Creator''. It is available via ''Start/All Programs/innovaphone/GSM Client/Configuration Creator''. | |||
[[Image:Mobility_GSM_Client_for_Windows_Mobile_cfgcreator-base.png]] | |||
To create the configuration files, follow these steps: | |||
* Enter your PBX address and credentials into the ''PBX'' field group. You can use either the administrator or viewer accounts or any PBX user with at least ''view'' rights. Please note that the program will not store the password you supply unless you tick the ''Save'' check mark | |||
* Select appropriate options in the ''Configuration Options'' field group. Unless you have a single extension configuration (see above), the only thing you should change here is the desired phone user interface language | |||
* Click the ''Validate PBX Config'' button in the ''Configuration Directories'' field group | |||
* Verify the output in the ''PBX Validation Result'' box | |||
* If the validation is OK, click the ''Create Mobile Configuration Files'' button | |||
If everything went OK, the program will create all configuration files | |||
and package them into Windows Mobile Cabinet (<code>.cab</code>) files. | |||
You will find this in the directory specified in the ''Configurations | |||
Root'' field in the ''Configuration Directories'' field group. However, | |||
there is normally no need to access these files manually. The can be | |||
installed semi-automatically (see below). | |||
The | ==== Validation Errors ==== | ||
The configuration program will do some efforts to detect inconsistencies | |||
in your PBX configuration. The configuration information found in the | |||
PBX as well as possibly detected errors are shown in the ''PBX Validation Result'' box. Be sure to scroll through the entire content and | |||
* make sure all users and mobile phones you expect are listed | |||
* no errors are reported | |||
== | Errors are shown prefixed with <code>==></code> and should be self-explaining. | ||
==== Multiple Configurations ==== | |||
If you want to maintain multiple configurations (e.g. to support | |||
multiple phone languages), you can use different names for them by | |||
putting them into the ''Configuration Name'' field in the' | |||
'Configuration Directories'' field group. | |||
They will be stored in subdirectories of the directory set in the | |||
''Configurations Root'' field in the ''Configuration Directories'' field | |||
group. | |||
=== Phone Installation === | |||
On each individual phone, you will need to install a number of so-called | |||
''packages'', which are available in the drop-down list next to the | |||
''Install CE Package'' button. | |||
[[Image:Mobility_GSM_Client_for_Windows_Mobile_package-select.png]] | |||
To install the complete ''GSM-Client'' application on the phone, use the | |||
''iAG GSM Client (full)'' package. This needs to be done once per | |||
phone. It needs to be re-done only if a new client software version is | |||
available. | |||
To install only the skins used in the ''GSM-Client'' application on the | |||
phone, use the ''iAG GSM Client (Skin only)'' package. This will rarely | |||
or never used though, but is provided to allow installation of your own | |||
skin package (if you decide to create one). | |||
=== | To install only the application executable on the phone, use the ''iAG | ||
GSM Client (binaries only)'' package. This may be an option if a hotfix | |||
version needs to be installed which has no changes in the skin data, as | |||
it is much smaller and thus much faster to install. | |||
During the beta phase, the installation packages will contain non-signed | |||
executables. These will normally neither install nor function. To work | |||
around this problem, the ''GSM Beta Patch'' package is provided. It | |||
will set some registry keys when installed which instruct windows mobile | |||
to skip the signature check. This should change with the release. You | |||
need to install this package once on your mobile and re-boot the mobile | |||
then. | |||
To install the full configuration on the phone, use the ''Config Name | |||
(xx.xx.xx)''. The full configuration must be installed on the phone | |||
initially and must be updated whenever there changes | |||
in | |||
* the users own mobile phone data | |||
* trunk line data | |||
* pbx data | |||
To install the current PBX extension table, use the ''Extension Name | |||
(xx.xx.xx)'' package. This needs to be done whenever there are new or | |||
changed extensions. | |||
''Name'' in the above configuration packages is the name you provided in | |||
the ''Configuration Name'' field of the ''Configuration Directories'' | |||
field group when creating the configuration. It is perfectly OK to | |||
always install the full ''Config ...'' package when the PBX | |||
configuration changes. Again, the ''Extensions'' subset will be much | |||
smaller (especially if there is a large number of mobile phones) and is | |||
provided for speed. | |||
''xx.xx.xx'' in the above configuration packages is the date you created | |||
the configuration package. | |||
To install a package, select it in the dropdown and click the ''Install | |||
CE Package'' button on the lower left. This will launch Microsoft's | |||
''ActiveSync'' utility to install the package on the mobile phone. | |||
Refer to the respective Microsoft documentation for detailed information | |||
on ''ActiveSync''. Be sure the phone is connected. | |||
When launched, ''ActiveSync'' will normally start the package | |||
installation on the phone right away: | |||
[[Image:Mobility_GSM_Client_for_Windows_Mobile_as-installing.png]] | |||
However, the installation process on the phone runs asynchronously, so | |||
you must check the phone itself too to see if the installation proceeds. | |||
[[Image:Mobility_GSM_Client_for_Windows_Mobile_phone-installing.png]] | |||
Also, the installer on the phone might ask some questions, e.g. where | |||
to install the package if you have additional internal or external | |||
memory cards on the phone. | |||
[[Image:Mobility_GSM_Client_for_Windows_Mobile_phone-asking.png]] | |||
If your phone asks for a destination, you must install all packages to | |||
the same destination always. Mixing destinations will result in a | |||
non-functional installation. if you need to move the installation from | |||
its original installation target (e.g. because you are running low on | |||
memory), you must de-install all the packages and then-reinstall to the | |||
new target. | |||
If the phone is not | |||
connected or if the package was installed before but disabled, it might | |||
not be installed. You need to examine ''ActiveSync''s list of installed | |||
software when the phone is connected and use the software installation | |||
GUI then. | |||
==== Windows CE CAB File Versioning ==== | |||
Windows CE apparently has no notion of a software version in its installer component. It assumes a cab file to install the same software only if it has the same ''Company Name'' and ''Application Name'' property. As a result, you cannot determine the version of an installed package. This is why we include the version (i.e. build) number in the ''Application Name'' property. | |||
While this has the beauty that you easily determine the version of the installed software as well as the version of the installed configuration, it has the downside that Windows CE will install any update as if it were different software. This does no harm however as long as you do not uninstall one of the packages. As they in fact share all the same files, uninstalling one of them will actually uninstall all of them (although Windows CE wouldn't know). It is OK thus to install subsequent versions of a package as long as you do not get confused when Windows CE shows multiple version as installed. If you prefer, you can choose to always first uninstall the previous version of a package manually before installing the new version. | |||
Also, you need to be aware that the packages provided overlap. That is for example, the ''iAG GSM Client (Skin only)'' is a subset of the ''iAG GSM Client (full)'' package. So if you uninstall ''Skin only'' the respective files are missing from the ''full'' package. Likewise, if you uninstall the ''full'' package, all the files from the ''Skin only'' package. Still, Windows CE will show the ''Skin only'' package as being installed. | |||
Here are the relationships: | |||
* ''full'' includes both ''Skin only'' and ''binaries only'' | |||
* ''Config'' includes ''Extensions'' | |||
==== Installing remotely ==== | |||
Windows CE cab files can be downloaded using its built-in web browser (Internet Explorer) and installed right away. Theoretically, all the packages can be installed this way, but we recommend installing the application and initial setup as described above and use the download method to provide updates to the extension list. | |||
For this to work, you need to provide the respective packages as <code>.cab</code> files (e.g. on an intranet web server). These are available in the ''My mobile configurations'' and ''Windows Mobile Installation Files'' directories (shortcuts available in the ''Start/All Programs/innovaphone/GSM Client'' menu). | |||
Here is how the <code>.cab</code> files map to the installation packages: | |||
{| | |||
| Package || CAB | |||
|- | |||
| iAG GSM Client (full) || innoGSM.PPC.cab and innoGSM.SP.cab, depending on phone platform | |||
|- | |||
| iAG GSM Client (binaries only) || innoGSMx.PPC.cab and innoGSMx.SP.cab, depending on phone platform | |||
|- | |||
| GSM Beta Patch || WMRegBetaSecurityPatch.cab | |||
|- | |||
| iAG GSM Client (Skin only) || innoCI.cab | |||
|- | |||
| Config Name (xx.xx.xxxx) || fullSetup.cab | |||
|- | |||
| Extensions Name (xx.xx.xxxx) || Extensions Name (xx.xx.xxxx) | |||
|} | |||
==== Providing your own Language ==== | |||
You can provide your own language. This is down by providing the following files | |||
* | * <code>\Programme\SD\GSMoIP\Languages\language.xml</code> where ''language'' is the name of your language. This file needs to be copied into the program directory used to install the program on the mobile phone. You can use one of the 3 files provided as a starter | ||
* <code>ODF-Menues-language.xml</code>, <code>ODF-Menues-language-MSN.xml</code> and <code>symbols-language.xml</code> where ''language'' is the name of your language. These files are used by the configuration creator and are thus packaged into the ''fullSetup.cab'' file automatically | |||
===Known Problems=== | |||
* The | * The ''GSM Client'' terminates during start-up showing an error message and a call stack trace (when clicking on ''Details'') | ||
This | This is most likely caused by a wrong PBX configuration resulting in | ||
wrong configuration files. Use the configuration creators ''Validate | |||
PBX Config'' button and make sure there are no errors shown. Review the | |||
configuration instructions above. | |||
* | * The user interface is not yet fully translated to the 3 languages provided (English, French, German). | ||
* New languages provided cannot be chosen in the configuration creator | |||
You need to replace one of the three standard languages for now. | |||
When your mobile phone does not work as expected, open a support ticket as usual and make sure you include the complete configuration (best send a PBX configuration file ''and'' the <code>fullSetup.cab</code> can file). | |||
== Releated Articles == | |||
[[Reference8:GSM Client Short User Guide]] | |||
[[Category:Howto|{{PAGENAME}}]] | [[Category:Howto|{{PAGENAME}}]] | ||
Revision as of 18:55, 8 October 2010
The GSM Client software is used for easy access to the mobility functions of V8 PBX from Windows Mobile phones. The GSM Client software is provided as a part of the gsm package which can be used to prepare Client configuration for transfer on the mobile device.
Applies To
This information applies to
- innovaphone PBX V8 hotfix6, Build 8050020 or later
- innovaphone gsm Package, Build 1045 or later
More Information
Requirements
On the Administrator's PC
- Operating System Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 or later
- .Net Framework 3.5
- ActiveSync 4.5 or later
- Firmware V8-based GSM Phone Client RC1 or later
On the Mobile Phone
The GSM Client software requires a Windows Mobile device. Create a backup of mobile device, before installing beta software!
- Windows Mobile 5.x, 6.x
- Smart Phone or Pocket PC
- CF 2.0 SP2 installed
- Internet Access (optional)
On the PBX
- Firmware V8 hotfix6 or later
- GSM-1 Client Licenses installed
- Mobility-8 Licenses installed
Overview
The GSM Client is an application that needs to be installed on the mobile phone. It replaces the standard phone application with a dedicated interface which converts the mobile phone in to a PBX Extension.
While this allows the client to provide PBX features in a useful way, it also has the drawback that the native phone application is no longer available. If this is not acceptable, there are other solutions available in the market which do not replace the native phone client, but add some functionality to it (cf. OptiCaller as an example). By design, such clients cannot offer the same functionality though.
The client assumes the existence and a specific configuration of the mobility functions in the PBX. It is therefore necessary to do the appropriate configuration on the PBX in order to use the GSM Client This configuration must be done using the PBX's standard administration facilities.
The GSM Client requires proper configuration to make the individual system characteristics (trunk lines, extensions ...) known to it. This configuration can be created automatically from the PBX data using the GSM-Client Configuration File Creator. This is a stand-alone PC application. It is intended to be used by the mobile phone administrator, end users will not need to work with the tool. The resulting configuration files are then transferred to the mobile phones using standard mechanisms provided by the phone's operating system (e.g. ActiveSync). The GSM-Client Configuration File Creator also greatly simplifies use of these mechanisms.
Once rollout to the mobile phone is done, configuration files have to be updated on the phones only rarely (e.g. if the trunk access changes). However, the PBX's extension list, which is also provided to the phone will obviously change more frequently. A mechanism to roll-out updates to this list is provided therefore.
The roll-out process for the GSM Client looks as follows thus
General preparation:
- download the latest gsm package from innovaphone's download page. It includes both the GSM-Client Configuration File Creator and the GSM Client for the platforms supported (currently Windows Mobile Smartphone and Windows Mobile PocketPC)
- install this package on the administrator's PC
- obtain and install mobility and gsm client licenses
- provide proper mobility objects configuration on the PBX
When this is done, rollout to the individual phones requires the following steps per phone
- add the individual mobile phone information to the user objects
- (re-)create GSM Client configuration files using the GSM-Client Configuration File Creator
- install the GSM Client program on the mobile phone
- install the configuration files created ion the second step on the mobile phone
When the extension list has changed on the PBX, the following steps are required to update the mobile phones
- (re-)create GSM Client configuration files using the GSM-Client Configuration File Creator
- install the extension file created on the previous step on the mobile phone
All mobile phones share the same set of configuration files, so it is not necessary to create separate configurations for each individual phone.
PBX Configuration
The following configurations must be done on the PBX
- Creation of the mobility objects
- Creation of the DTMF features objects
- Attribution of the respective trunk line objects
- Installation of proper GSM-1 and Mobility-8 licenses
- Attribution of the respective user forking entries
Numbering Plan
Mobility is based on a number of feature codes which are used by the mobile phone to access the features. These codes are in fact objects in the PBX (Mobility and DTMF-Feature) which need to be called. As a result, these feature codes each require individual extensions in the PBX's numbering plan. To make things worse, the GSM network does not carry * or # digits in a called number, so the extensions to be used must be plain numbers.
You will need to reserve a number of extensions with a common prefix thus in your PBX's numbering plan. If this is not possible (e.g. because you reside in a country with a fixed numbering plan and you don't have a block large enough to allocate the numbers), you may revert to use a single extension in your numbering plan. Be aware though that this will result in
- cost charged by your mobile operator for invoking features (some of the features are normally invoked by calling an extension without accepting the call, which should be free. When using a single extension, all features are invoked by calling this number, accepting the call and then dialling the desired feature using in-band DTMF tones)
- longer execution time for most of the features invoked
You need thus determine an available prefix for the feature codes within you PBX's numbering plan (say 54).
For the remainder of this article, we will refer to this prefix as mobility-prefix.
Mobility Object
There must be a mobility object on each PBX system with a mobility enabled user (that is, a user with an integrated mobile phone). The easiest way to achieve this is to create a mobility object with Node and PBX left empty.
The Number property of the mobility object must be set to the mobility-prefix chosen plus literal 9.
This will result in one mobility object per PBX which has the PBX's node number as a prefix. Assuming the PBX's node number is 81, the full number of the mobility object in our example would be 81549.
DTMF-Features Object
Again, there must be a DTMF-Features object on each PBX system with a mobility enabled user (that is, a user with an integrated mobile phone). The easiest way to achieve this is to create a DTMF-Features object with Node and PBX left empty.
The DTMF-Features object itself does not have a Number property. Instead, the individual features have one. The features must have fixed numbers according to the following table:
| CFU Activate | mobility-prefix10$# |
Deactivate | mobility-prefix11
|
| CFB Activate | mobility-prefix12$# |
Deactivate | mobility-prefix13
|
| CFNR Activate | mobility-prefix14$# |
Deactivate | mobility-prefix15
|
| Pickup Group | mobility-prefix16 |
Directed | mobility-prefix17$#
|
| Park | mobility-prefix18$ |
Unpark | mobility-prefix19$
|
| Park To | mobility-prefix20$(1)$# |
Unpark From | mobility-prefix21$(1)$#
|
| Call Completion Busy | mobility-prefix22$# |
Cancel | mobility-prefix23$#
|
| Join Group | mobility-prefix24$# |
Leave | mobility-prefix25$#
|
| Join All Groups | mobility-prefix26 |
Leave | mobility-prefix27
|
| Enable mobility | mobility-prefix28 |
Disable mobility | mobility-prefix29
|
| Enable mobility cw | mobility-prefix30 |
Disable mobility cw | mobility-prefix31
|
| Set presence | mobility-prefix32$(1)$(1) |
Unset presence | mobility-prefix33$(1)
|
In our example, the list of mobility related objects should look like this:
DTMF-Features#call_completion 81.5422 DTMF-Features#cancel_cc 81.5423 DTMF-Features#cfb_activate 81.5412 DTMF-Features#cfb_deactivate 81.5413 DTMF-Features#cfnr_activate 81.5414 DTMF-Features#cfnr_deactivate 81.5415 DTMF-Features#cfu_activate 81.5410 DTMF-Features#cfu_deactivate 81.5411 DTMF-Features#disable_mobility 81.5429 DTMF-Features#disable_mobility_cw 81.5431 DTMF-Features#enable_mobility 81.5428 DTMF-Features#enable_mobility_cw 81.5430 DTMF-Features#join_all_groups 81.5426 DTMF-Features#join_group 81.5424 DTMF-Features#leave_all_groups 81.5427 DTMF-Features#leave_group 81.5425 DTMF-Features#park 81.5418 DTMF-Features#park_to 81.5420 DTMF-Features#pickup_directed 81.5417 DTMF-Features#pickup_group 81.5416 DTMF-Features#set_presence 81.5432 DTMF-Features#unpark 81.5419 DTMF-Features#unpark_from 81.5421 DTMF-Features#unset_presence 81.5433 Mobility 81.549
Trunk Lines
You do not need to create new trunk line objects for mobility. Instead, you need to attribute the existing objects to make their E.164 number known to the system.
For this, you need to edit each trunk line and put the lines international number into its Description property. This must be done using the international number format, starting with +. Assuming the trunk line in our example has subscriber number 73009, area code 7031 and county code 49, you would specify +49703173009. Do not add your switchboard extension (usually 0 here!).
Users
To enable mobility for a user, you need to
- make sure you have both Mobility-8 and GSM-1 licenses available. As usual, test licenses are available from within my.innovaphone
- add a forking destination for each mobile phone the user wants to use with mobility
- make the users mobile phone numbers known to the system
- make the users mobile phone IMEI known to the system
Put the phone's number into the No property. This number must be
specified exactly as it would be received by the PBX when this phone
calls in. That is, it is the number including GSM carrier prefix and
trunk prefix, no country code, no +. Assuming the users
mobile number is 017247110815 and the trunk line prefix in
your PBX is 0, you would specify
0017247110815.
Put the phone's IMEI into the Device property of the respective
forking entry. The IMEI will always be a 15-digit number, such as e.g.
354503021446625. If your IMEI is 17-digits instead, leave
out the last 2 digits simply. In Windows Mobile, you can find the
device's IMEI number in the Settings/System/Device Information
(Einstellungen/System/Geräte-Information). The IMEI may also be
display by dialling *#06# from within the phone's native
phone application.
Make sure the GSM-License check mark is ticked for the respective forking entry!
Configuration Generation
Download the gsm package from innovaphone's download page. Install pcsetup.msi and follow the instructions in Start/Applications/innovaphone/GSM Client/Readme.
The GSM Client configuration files can be generated using the GSM-Client Configuration File Creator. It is available via Start/All Programs/innovaphone/GSM Client/Configuration Creator.
To create the configuration files, follow these steps:
- Enter your PBX address and credentials into the PBX field group. You can use either the administrator or viewer accounts or any PBX user with at least view rights. Please note that the program will not store the password you supply unless you tick the Save check mark
- Select appropriate options in the Configuration Options field group. Unless you have a single extension configuration (see above), the only thing you should change here is the desired phone user interface language
- Click the Validate PBX Config button in the Configuration Directories field group
- Verify the output in the PBX Validation Result box
- If the validation is OK, click the Create Mobile Configuration Files button
If everything went OK, the program will create all configuration files
and package them into Windows Mobile Cabinet (.cab) files.
You will find this in the directory specified in the Configurations
Root field in the Configuration Directories field group. However,
there is normally no need to access these files manually. The can be
installed semi-automatically (see below).
Validation Errors
The configuration program will do some efforts to detect inconsistencies in your PBX configuration. The configuration information found in the PBX as well as possibly detected errors are shown in the PBX Validation Result box. Be sure to scroll through the entire content and
- make sure all users and mobile phones you expect are listed
- no errors are reported
Errors are shown prefixed with ==> and should be self-explaining.
Multiple Configurations
If you want to maintain multiple configurations (e.g. to support multiple phone languages), you can use different names for them by putting them into the Configuration Name field in the' 'Configuration Directories field group.
They will be stored in subdirectories of the directory set in the Configurations Root field in the Configuration Directories field group.
Phone Installation
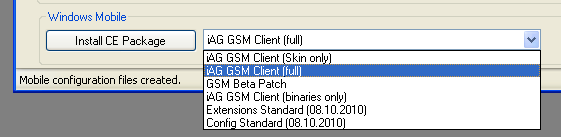
On each individual phone, you will need to install a number of so-called packages, which are available in the drop-down list next to the Install CE Package button.
To install the complete GSM-Client application on the phone, use the iAG GSM Client (full) package. This needs to be done once per phone. It needs to be re-done only if a new client software version is available.
To install only the skins used in the GSM-Client application on the phone, use the iAG GSM Client (Skin only) package. This will rarely or never used though, but is provided to allow installation of your own skin package (if you decide to create one).
To install only the application executable on the phone, use the iAG GSM Client (binaries only) package. This may be an option if a hotfix version needs to be installed which has no changes in the skin data, as it is much smaller and thus much faster to install.
During the beta phase, the installation packages will contain non-signed executables. These will normally neither install nor function. To work around this problem, the GSM Beta Patch package is provided. It will set some registry keys when installed which instruct windows mobile to skip the signature check. This should change with the release. You need to install this package once on your mobile and re-boot the mobile then.
To install the full configuration on the phone, use the Config Name (xx.xx.xx). The full configuration must be installed on the phone initially and must be updated whenever there changes in
- the users own mobile phone data
- trunk line data
- pbx data
To install the current PBX extension table, use the Extension Name (xx.xx.xx) package. This needs to be done whenever there are new or changed extensions.
Name in the above configuration packages is the name you provided in the Configuration Name field of the Configuration Directories field group when creating the configuration. It is perfectly OK to always install the full Config ... package when the PBX configuration changes. Again, the Extensions subset will be much smaller (especially if there is a large number of mobile phones) and is provided for speed.
xx.xx.xx in the above configuration packages is the date you created the configuration package.
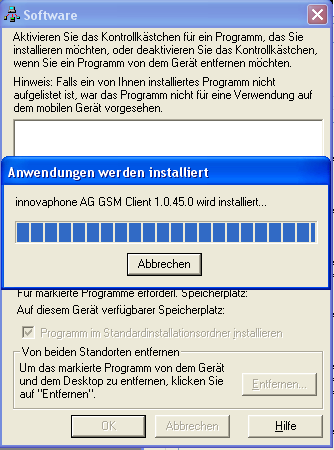
To install a package, select it in the dropdown and click the Install CE Package button on the lower left. This will launch Microsoft's ActiveSync utility to install the package on the mobile phone. Refer to the respective Microsoft documentation for detailed information on ActiveSync. Be sure the phone is connected.
When launched, ActiveSync will normally start the package installation on the phone right away:
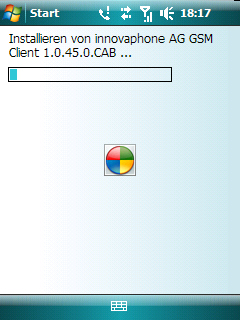
However, the installation process on the phone runs asynchronously, so you must check the phone itself too to see if the installation proceeds.
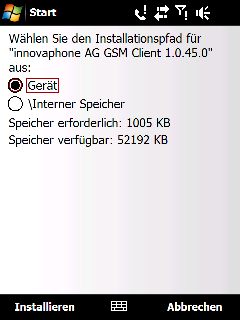
Also, the installer on the phone might ask some questions, e.g. where to install the package if you have additional internal or external memory cards on the phone.
If your phone asks for a destination, you must install all packages to the same destination always. Mixing destinations will result in a non-functional installation. if you need to move the installation from its original installation target (e.g. because you are running low on memory), you must de-install all the packages and then-reinstall to the new target.
If the phone is not connected or if the package was installed before but disabled, it might not be installed. You need to examine ActiveSyncs list of installed software when the phone is connected and use the software installation GUI then.
Windows CE CAB File Versioning
Windows CE apparently has no notion of a software version in its installer component. It assumes a cab file to install the same software only if it has the same Company Name and Application Name property. As a result, you cannot determine the version of an installed package. This is why we include the version (i.e. build) number in the Application Name property.
While this has the beauty that you easily determine the version of the installed software as well as the version of the installed configuration, it has the downside that Windows CE will install any update as if it were different software. This does no harm however as long as you do not uninstall one of the packages. As they in fact share all the same files, uninstalling one of them will actually uninstall all of them (although Windows CE wouldn't know). It is OK thus to install subsequent versions of a package as long as you do not get confused when Windows CE shows multiple version as installed. If you prefer, you can choose to always first uninstall the previous version of a package manually before installing the new version.
Also, you need to be aware that the packages provided overlap. That is for example, the iAG GSM Client (Skin only) is a subset of the iAG GSM Client (full) package. So if you uninstall Skin only the respective files are missing from the full package. Likewise, if you uninstall the full package, all the files from the Skin only package. Still, Windows CE will show the Skin only package as being installed.
Here are the relationships:
- full includes both Skin only and binaries only
- Config includes Extensions
Installing remotely
Windows CE cab files can be downloaded using its built-in web browser (Internet Explorer) and installed right away. Theoretically, all the packages can be installed this way, but we recommend installing the application and initial setup as described above and use the download method to provide updates to the extension list.
For this to work, you need to provide the respective packages as .cab files (e.g. on an intranet web server). These are available in the My mobile configurations and Windows Mobile Installation Files directories (shortcuts available in the Start/All Programs/innovaphone/GSM Client menu).
Here is how the .cab files map to the installation packages:
| Package | CAB |
| iAG GSM Client (full) | innoGSM.PPC.cab and innoGSM.SP.cab, depending on phone platform |
| iAG GSM Client (binaries only) | innoGSMx.PPC.cab and innoGSMx.SP.cab, depending on phone platform |
| GSM Beta Patch | WMRegBetaSecurityPatch.cab |
| iAG GSM Client (Skin only) | innoCI.cab |
| Config Name (xx.xx.xxxx) | fullSetup.cab |
| Extensions Name (xx.xx.xxxx) | Extensions Name (xx.xx.xxxx) |
Providing your own Language
You can provide your own language. This is down by providing the following files
\Programme\SD\GSMoIP\Languages\language.xmlwhere language is the name of your language. This file needs to be copied into the program directory used to install the program on the mobile phone. You can use one of the 3 files provided as a starterODF-Menues-language.xml,ODF-Menues-language-MSN.xmlandsymbols-language.xmlwhere language is the name of your language. These files are used by the configuration creator and are thus packaged into the fullSetup.cab file automatically
Known Problems
- The GSM Client terminates during start-up showing an error message and a call stack trace (when clicking on Details)
This is most likely caused by a wrong PBX configuration resulting in wrong configuration files. Use the configuration creators Validate PBX Config button and make sure there are no errors shown. Review the configuration instructions above.
- The user interface is not yet fully translated to the 3 languages provided (English, French, German).
- New languages provided cannot be chosen in the configuration creator
You need to replace one of the three standard languages for now.
When your mobile phone does not work as expected, open a support ticket as usual and make sure you include the complete configuration (best send a PBX configuration file and the fullSetup.cab can file).