Reference8:Configuration/LINUX/General: Difference between revisions
| (30 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The fundamental operating modes of | The fundamental operating modes of Linux are configured on this page. | ||
The Linux OS can be startet on selected platforms as a secondary operating system that runs application specific tasks. | The Linux OS can be startet on selected platforms as a secondary operating system that runs application specific tasks. | ||
Linux and the innovaphone OS coexist on the device and share the resources like memory and cpu time. | Linux and the innovaphone OS coexist on the device and share the resources like memory and cpu time. | ||
Note: LINUX is only as Beta for experimental use at V8 available | |||
==Supported platforms== | ==Supported platforms== | ||
Linux is | Linux is currently supported as a beta on the IP6000 in big or little-endian. The default endian of the IP6000 is big-endian. | ||
==IP6000 little endian== | ==IP6000 little-endian== | ||
Common | Common Linux distributions run in little-endian, the IP6000 CPU usually runs in big-endian. | ||
To support little endian | To support little-endian Linux a little-endian IP6000 firmware is available. | ||
To install this firmware the LDAP directory and the VARS need to be changed to little endian format. | To install this firmware the LDAP directory and the VARS need to be changed to little-endian format. | ||
The procedure to install the little endian IP6000 firmware version is: | The procedure to install the little-endian IP6000 firmware version is: | ||
* Backup configuration | * Backup configuration | ||
* Install latest | * Install latest boot code that allows to boot little-endian IP6000 firmware. | ||
* Install latest IP6000 firmware that supports migration to littleendian | * Install latest IP6000 firmware that supports migration to littleendian | ||
* clear the flash memory with http://addr/!mod+cmd+FLASHMAN0+reset+all+erase | * clear the flash memory with http://addr/!mod+cmd+FLASHMAN0+reset+all+erase | ||
* Upload the little endian firmware to DRAM ( ip6000-le.bin ) | * Upload the little endian firmware to DRAM ( ip6000-le.bin ) | ||
* Now the little endian code is running... | * Now the little-endian code is running... | ||
* Upload ip6000-le.bin to flash. | * Upload ip6000-le.bin to flash. | ||
* Restore configuration | * Restore configuration | ||
The | The IP6000 little-endian version has some restrictions: boot code update is not possible, certificate key invalidation is not supported. | ||
To install the big endian over the little endian version it is also needed to clear the flash, upload the | To install the big-endian over the little-endian version it is also needed to clear the flash, upload the big-endian version to DRAM, and then flash the big-endian version. | ||
==Memory partitioning== | ==Memory partitioning== | ||
The innovaphone OS can reserve memory for Linux. | The innovaphone OS can reserve memory for Linux and switches the Linux menus on. | ||
This is done with the commands | This is done with the commands | ||
| Line 35: | Line 37: | ||
http://addr/!reset | http://addr/!reset | ||
== Configuration == | == Configuration == | ||
== | === ETH2 - virtual network connction for Linux === | ||
* DHCP: Mode Server | * DHCP: Mode Server | ||
* IP: IP Address z.B. 172.16.14.253 | * IP: IP Address z.B. 172.16.14.253 | ||
* IP: IP Network Mask z.B 255.255.255.252 | * IP: IP Network Mask z.B 255.255.255.252 | ||
* IP: Proxy ARP enable, also for outgoing | * IP: Proxy ARP enable, also for outgoing network interface ETH0 or ETH1 | ||
* DHCP-Server: First Address | * DHCP-Server: First Address and Last Address e.g. 172.16.14.254 | ||
* DHCP-Server: Network Mask 255.255.0.0 | * DHCP-Server: Network Mask 255.255.0.0 | ||
* DHCP-Server: Default Gateway 172.16.0.1 | * DHCP-Server: Default Gateway 172.16.0.1 | ||
== Start Linux == | === Start Linux === | ||
For starting Linux a | For starting Linux a kernel binary must be uploaded or be provided via the compact flash (CF) card. Via the kernel command line you tell the kernel where the root file system is. This can be uploaded or be available via the CF card. It will be used as temporary RAM disk, or as whole partition on the CF card. | ||
=== Linux with | ==== Linux with root file system starting in a RAM disk ==== | ||
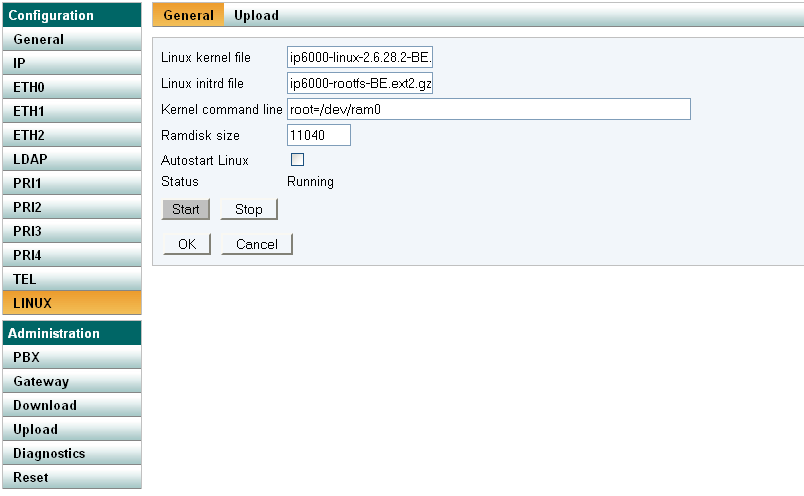
* Linux kernel file: | * Linux kernel file: e.g. ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.bin | ||
* Linux initrd file: rootfs | * Linux initrd file: e.g. ip6000-rootfs-BE.ext2.gz | ||
* Kernel command line: root=/dev/ram0 | * Kernel command line: root=/dev/ram0 | ||
* Ramdisk size in kBytes: 11040 | * Ramdisk size in kBytes: 11040 | ||
[[ | [[Image:Linux-menu.png]] | ||
=== Linux with | ==== Linux with root file system on the compact flash card ==== | ||
* Linux kernel file: | * Linux kernel file: e.g. ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.bin | ||
* Linux initrd file: | * Linux initrd file: | ||
* Kernel command line: root=/dev/sda2 | * Kernel command line: root=/dev/sda2 | ||
* Ramdisk size in kBytes: | * Ramdisk size in kBytes: | ||
== Copy Linux to the | === Copy Linux to the compact flash card === | ||
The root system shows a file system on the CF card. Linux will be started with the root file system in the RAM disk. | |||
With telnet you can connect to the Linux system: | |||
telnet 172.16.14.253 | telnet 172.16.14.253 | ||
| Line 87: | Line 77: | ||
No password. | No password. | ||
Mounting of the CF | Mounting of the CF card and copy the data: | ||
su (no password) | su (no password) | ||
mount /dev/sda /mnt | mount /dev/sda /mnt | ||
cp /mnt/ | cp /mnt/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2.gz /tmp/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2.gz | ||
umount /dev/sda | umount /dev/sda | ||
Build a partition on the CF | Build a partition on the CF card: | ||
fdisk /dev/sda | fdisk /dev/sda | ||
The first primary partition can be a WIN95 (LBA), the second a | The first primary partition can be a WIN95 (LBA), the second a Linux partition. A swap partition will be initialized searched on the fourth position. | ||
Format partition, mounting and copy the root file system: | |||
mkfs.ext2 /dev/sda2 | mkfs.ext2 /dev/sda2 | ||
gunzip /tmp/ | gunzip /tmp/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2.gz | ||
mkdir /tmp/root | mkdir /tmp/root | ||
mount /tmp/ | mount /tmp/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2 /tmp/root -o loop | ||
mount /dev/sda2 /mnt | mount /dev/sda2 /mnt | ||
cp -r /tmp/root /mnt | cp -r /tmp/root /mnt | ||
umount /tmp/ | umount /tmp/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2 | ||
umount /dev/sda2 | umount /dev/sda2 | ||
Latest revision as of 19:08, 18 November 2009
The fundamental operating modes of Linux are configured on this page. The Linux OS can be startet on selected platforms as a secondary operating system that runs application specific tasks. Linux and the innovaphone OS coexist on the device and share the resources like memory and cpu time.
Note: LINUX is only as Beta for experimental use at V8 available
Supported platforms
Linux is currently supported as a beta on the IP6000 in big or little-endian. The default endian of the IP6000 is big-endian.
IP6000 little-endian
Common Linux distributions run in little-endian, the IP6000 CPU usually runs in big-endian. To support little-endian Linux a little-endian IP6000 firmware is available. To install this firmware the LDAP directory and the VARS need to be changed to little-endian format. The procedure to install the little-endian IP6000 firmware version is:
- Backup configuration
- Install latest boot code that allows to boot little-endian IP6000 firmware.
- Install latest IP6000 firmware that supports migration to littleendian
- clear the flash memory with http://addr/!mod+cmd+FLASHMAN0+reset+all+erase
- Upload the little endian firmware to DRAM ( ip6000-le.bin )
- Now the little-endian code is running...
- Upload ip6000-le.bin to flash.
- Restore configuration
The IP6000 little-endian version has some restrictions: boot code update is not possible, certificate key invalidation is not supported.
To install the big-endian over the little-endian version it is also needed to clear the flash, upload the big-endian version to DRAM, and then flash the big-endian version.
Memory partitioning
The innovaphone OS can reserve memory for Linux and switches the Linux menus on. This is done with the commands
http://addr/!config+flags+L...
Configuration
ETH2 - virtual network connction for Linux
- DHCP: Mode Server
- IP: IP Address z.B. 172.16.14.253
- IP: IP Network Mask z.B 255.255.255.252
- IP: Proxy ARP enable, also for outgoing network interface ETH0 or ETH1
- DHCP-Server: First Address and Last Address e.g. 172.16.14.254
- DHCP-Server: Network Mask 255.255.0.0
- DHCP-Server: Default Gateway 172.16.0.1
Start Linux
For starting Linux a kernel binary must be uploaded or be provided via the compact flash (CF) card. Via the kernel command line you tell the kernel where the root file system is. This can be uploaded or be available via the CF card. It will be used as temporary RAM disk, or as whole partition on the CF card.
Linux with root file system starting in a RAM disk
- Linux kernel file: e.g. ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.bin
- Linux initrd file: e.g. ip6000-rootfs-BE.ext2.gz
- Kernel command line: root=/dev/ram0
- Ramdisk size in kBytes: 11040
Linux with root file system on the compact flash card
- Linux kernel file: e.g. ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.bin
- Linux initrd file:
- Kernel command line: root=/dev/sda2
- Ramdisk size in kBytes:
Copy Linux to the compact flash card
The root system shows a file system on the CF card. Linux will be started with the root file system in the RAM disk. With telnet you can connect to the Linux system:
telnet 172.16.14.253
Loginname: default No password.
Mounting of the CF card and copy the data:
su (no password) mount /dev/sda /mnt cp /mnt/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2.gz /tmp/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2.gz umount /dev/sda
Build a partition on the CF card:
fdisk /dev/sda
The first primary partition can be a WIN95 (LBA), the second a Linux partition. A swap partition will be initialized searched on the fourth position.
Format partition, mounting and copy the root file system:
mkfs.ext2 /dev/sda2 gunzip /tmp/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2.gz mkdir /tmp/root mount /tmp/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2 /tmp/root -o loop mount /dev/sda2 /mnt cp -r /tmp/root /mnt umount /tmp/ip6000-linux-2.6.28.2-BE.ext2 umount /dev/sda2